
CISO Monthly Roundup, July 2023: TOITOIN targets LATAM, Qakbot dissected, Super Cloud 3, Zenith Live ‘23, and malicious ChatGPT variants
Aug 14, 2023
The July CISO Monthly Roundup explores the TOITOIN Trojan, QakBot, previews Zenith Live '23, and more.
The CISO Monthly Roundup provides the latest threat research from Deepen Desai and the ThreatLabz team, along with insights on other cyber-related subjects. Over the past month, ThreatLabz analyzed the TOITOIN trojan and dissected Qakbot. Deepen Desai, Zscaler’s Global CISO and Head of Security Research & Operations shared security insights at Super Cloud3, Zenith Live ‘23, and warned about the rise of malicious Chat GPT variants.
TOITOIN trojan unleashed on LATAM region
In May 2023, ThreatLabz researchers discovered numerous malware samples being trafficked in ZIP archives. These archives, hosted on Amazon EC2, were part of a TOITOIN malware campaign targeting the Latin American (LATAM) region. Using Amazon EC2 instances allows threat actors to evade domain-based detections, and makes detecting and blocking their activities more difficult. The TOITOIN campaign uses well-crafted phishing emails, posing as payment notifications, to launch a multi-stage infection chain.
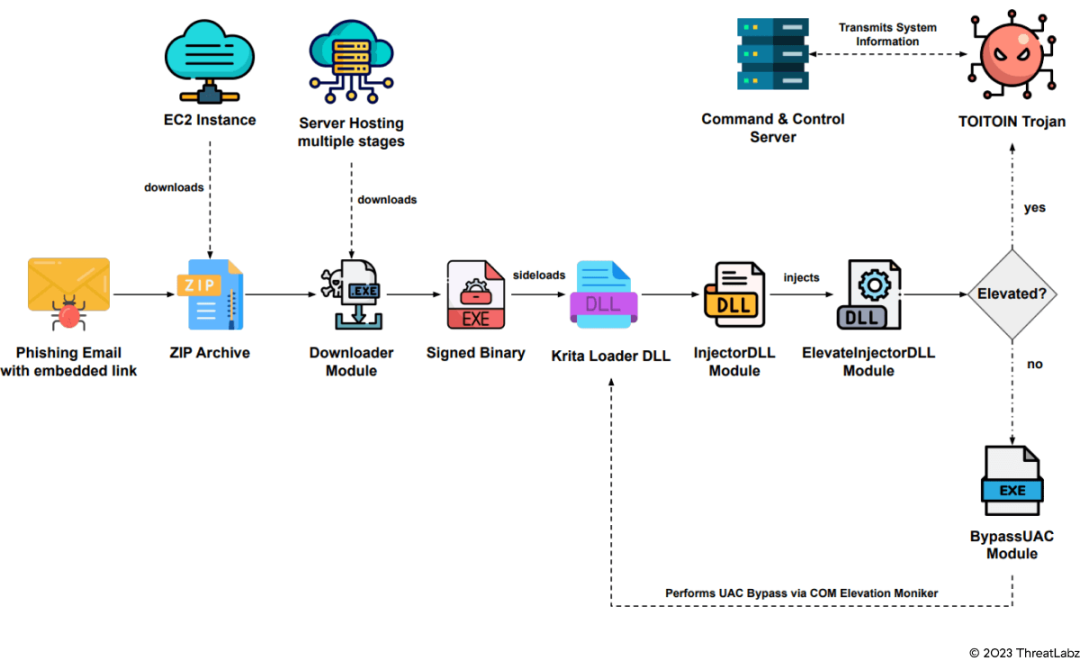
The TOITOIN campaign uses several custom-developed modules in its infection chain:
- The downloader module evades sandboxes, establishes persistence, and loads additional threats
- Krita Loader DLL is sideloaded using a signed binary, and launches the InjectorDLL module
- InjectorDLL injects another module, ElevateInjectorDLL into the explorer.exe process
- ElevateInjectorDLL performs process hollowing and, based on process privileges, injects either the TOITOIN trojan or BypassUAC module.
- BypassUAC can bypass user account control (UAC) and launch the Krita Loader DLL using admin privileges.
The TOITOIN trojan uses custom XOR decryption routines to decode the configuration file containing the C2’s address. It sends the C2 system information, browser details, and information related to core.exe (Topaz OFD - Protection Module) if it is present on the target machine.
Read the full analysis on TOITOIN
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage: Zscaler Posture Control, Advanced Cloud Sandbox, Advanced Threat Protection, SSL Inspection.
Hibernating Qakbot: A comprehensive study and campaign analysis
Qakbot, the infamous banking trojan, has been used to attack institutions worldwide since 2007. Its adaptability, obfuscation capabilities, and sophistication make it a formidable adversary and are responsible for its longevity. ThreatLabz has monitored Qakbot for years as part of our commitment to observe and report on active malware campaigns. Recently, we published research on how the malware uses OneNote files as an attack vector.
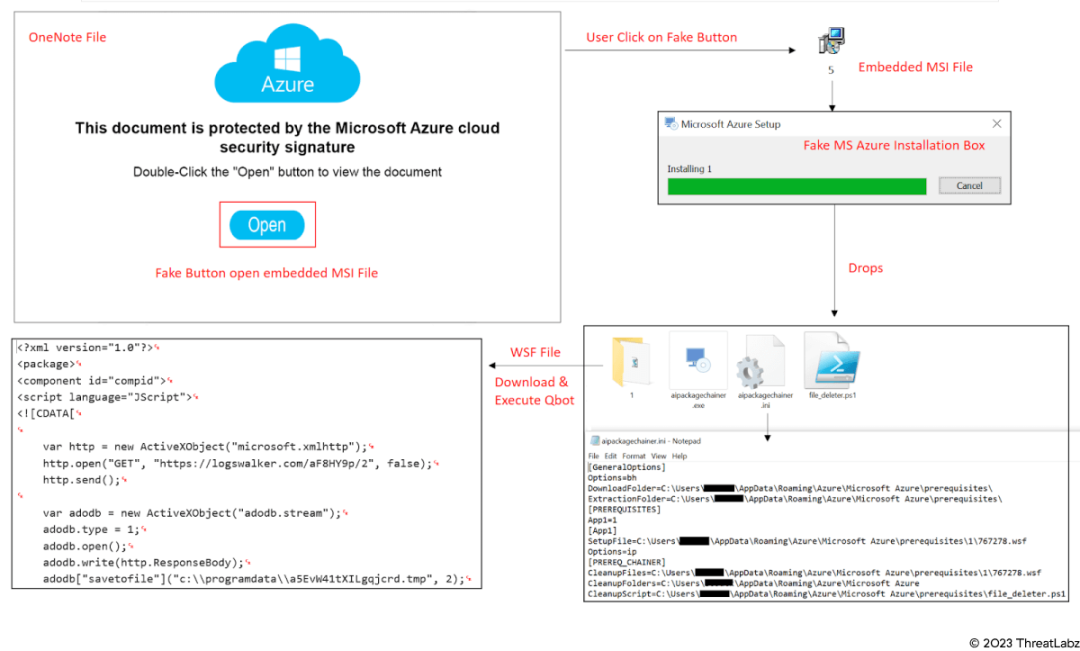
Our recent research examines Qakbot’s ability to use multiple attack chains, abuse several file formats, and adopt new obfuscation methods over time. We look at the recent OneNote campaign and see adversaries who discover new ways of exploiting file vulnerabilities despite being targeted by specific security measures. Another aspect we explore is its global reach. Qakbot has highly active C2 infrastructure in multiple countries and is capable of hitting targets worldwide. While Qakbot activity has experienced a recent decline, organizations should continue awareness training and take proactive mitigation steps to safeguard against this threat.
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage: Advanced Cloud Sandbox, Advanced Threat Protection, SSL Inspection.
Super Cloud 3
Supercloud is a term that refers to the unification of all enterprise cloud architecture into a single manageable interface. Recently, I had the honor to join our CEO Jay Chaudhry at the Supercloud 3 event to discuss security issues, zero trust, and AI. The event was hosted by theCUBE and SiliconANGLE, two organizations dedicated to circulating tech thought leadership worldwide.

The conversation covered a variety of topics involving cloud security, issues with legacy networks, and embracing emerging technologies. The panel discussed the value of zero trust and attack surface management, and covered questions organizations should ask about their own cloud security. Another hot topic was AI, where our conversation touched on security signal correlation in the supercloud, defender’s advantage, and benefits of merging generative and predictive models.
Explore zero trust, AI security, and the supercloud
Zenith Live ‘23
Zenith Live is Zscaler’s premiere global event where we gather employees, customers, and partners to discuss the latest topics in cybersecurity. I presented a real ransomware attack that breached a large publicly traded company as part of my Zenith Live '23 security innovation keynote. This attack was attributed to the DarkAngels Ransowmare group, known for targeting the finance, technology, education, and healthcare industry verticals.
I revealed the consequences one company experienced after the threat group gained enterprise access by phishing a single user. The target organization used a flat, traditional network architecture, allowing the attackers to use lateral movement to access and steal 24TB of information. The company ultimately paid $5.5 million to the threat group, who then provided the company with a breakdown of how they carried out the attack.

Key Takeaways from CISO Perspective:
One of the primary reasons ransomware attacks continue to be successful is the widespread usage of VPNs (on-prem/cloud) and legacy network architecture. The traditional flat network model allows attackers to move laterally within victim environments. To safeguard against these evolving attacks, it is critical for organizations to:
- Eliminate the use of VPNs
- Prioritize user-to-app segmentation
- Implement an in-line contextual data loss prevention engine with full TLS inspection
Another important step is to adopt a zero trust platform like the Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange rather than having several point products that require out-of-band correlation to generate a response. The time it takes to respond to an incident can make the difference between a single incident vs. an organizational breach. A zero trust platform detects and responds to attacks significantly faster than analysts who are attempting to leverage a wide range of third-party tools.
The next round of Zenith Live ‘23 events will be held in the Asia Pacific (APAC) region on the following dates:
Zenith Live Sydney
Tuesday, 19 September | The Establishment | Sydney, Australia
Zenith Live Singapore
Tuesday, 26 September | The Arts House | Singapore
Zenith Live Mumbai
Friday, 29 September | JW Marriott | Mumbai, India
I hope we will see you there.
Risk360 - New product for CISOs by a CISO
As part of my Zentih Live ‘23 technology innovation keynote, I announced the launch of Zscaler Risk360 - the industry’s most comprehensive and actionable risk framework that provides risk quantification and actionable remediations. Risk360 measures your organization’s risk across four key stages of the attack chain and provides a holistic view of your risk profile.
Our security team and data scientists identified 100+ risk-contributing factors that take into account how your organization's security controls are configured, their maturity, and behaviors observed in your environment. All of these factors play a role when computing your organization’s risk.
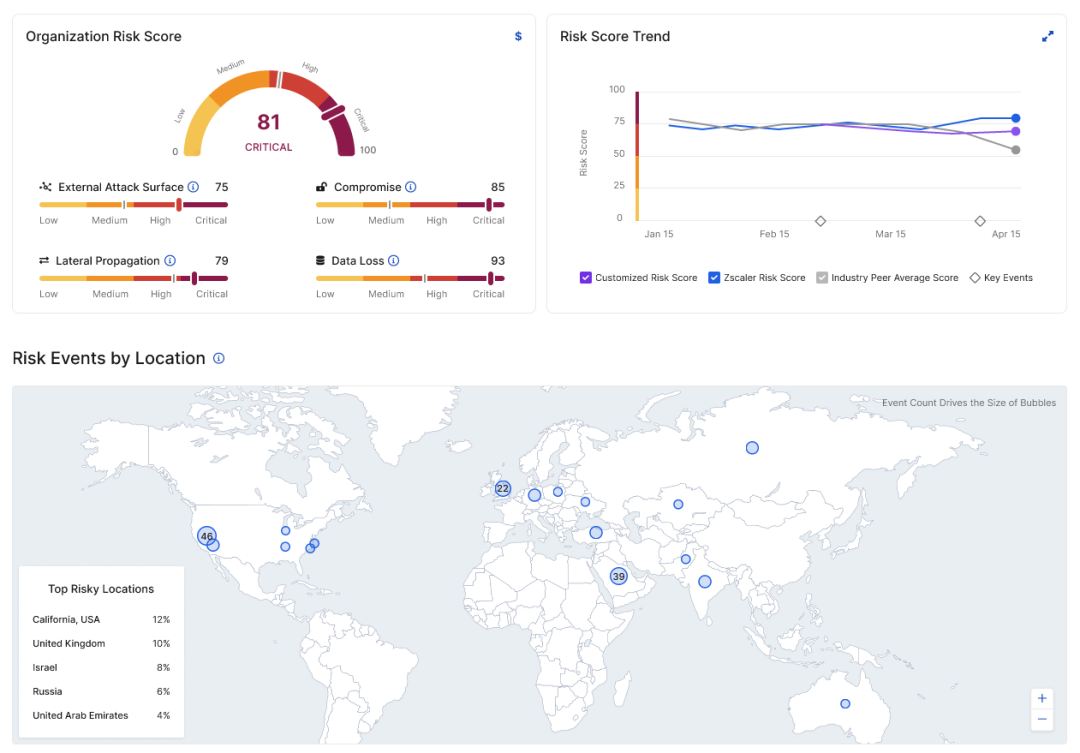
In order to further help prioritize your remediation efforts, the product classifies risk into four major entities that CISOs care about - workforce, third parties, applications, and assets. Risk360 continuously shows how your organization’s risk is trending compared to your industry peers. This allows you to measure your risk mitigation progress in real time. It also has filtering options that drill down into the top drivers of organizational cyber risk, estimate financial losses, and offer remediation recommendations.
Generative AI innovation
Zscaler is delivering new artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) capabilities to customers. We have long used AI/ML to recommend security policies, classify data, identify risks and segment users and applications. We are also using it to prevent data loss (including through LLM prompts), assess AI application risk scores, and monitor URLs to assess online AI usage. These capabilities are key for protecting enterprises tip-toeing into the world of ChatGPT and similar AI applications. Other newly-announced Zscaler AI technologies include:
- Security Autopilot™ - A proactive tool that searches for vulnerabilities in dynamic and changing cloud-based policies.
- Zscaler Navigator™ - A natural language interface that helps customers securely access Zscaler products and relevant documentation
- Multi-Modal DLP: Integrates generative AI and multi-modal capabilities into our current DLP offering, extending protective coverage to audio and video files
The rise of malicious LLM variants
It was inevitable that AI, like any tool, would be misused by people seeking personal gain. If you are staying on top of the AI news cycle, you have probably heard of WormGPT, DarkBERT, and FraudGPT. These generative AI models, circulating on the dark web, are trained to assist attackers in conducting malicious cyber operations. Offloading aspects of the attack chain to AI makes conducting large-scale cyberattacks easier, especially in cases where language barriers previously presented a challenge.

One area where AI excels in malicious operations is business email compromise (BEC) attacks. AIs like WormGPT make it easy for threat actors to compose a phishing email in their native language then generate a convincing translation of it in their target’s language. Generative AI creates emails with exceptional grammar and a convincing tone, increasing the likelihood of successful phishing attacks. AIs also boast capabilities beyond phishing, including malicious code generation, malware obfuscation, vulnerability detection, and hacker tool creation. While these advertised abilities have not yet been documented in the wild, it seems only a matter of time before enterprises will be forced to address them. A true zero trust architecture is needed to guard against these sophisticated attacks.
About ThreatLabz
ThreatLabz is the embedded research team at Zscaler. This global team includes security experts, researchers, and network engineers responsible for analyzing and eliminating threats across the Zscaler security cloud and investigating the global threat landscape. The team shares its research and cloud data with the industry at large to help promote a safer internet.
The Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange
Zscaler manages the world’s largest security cloud. Each day, Zscaler blocks over 150 million threats to its 6000+ customers, securing over 240 billion web transactions daily. The Zscaler ThreatLabz security research team uses state-of-the-art AI and machine-learning technology to analyze Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange traffic and share its findings.
What to read next:
Into the abyss: How a dark web LLM could enhance our cybersecurity
Crawl, walk, and run your way to more effective CASB policy creation
Recommended
