
CXO Monthly Roundup, October 2025: Mobile, IoT, & OT ThreatLabz report, non-web Protocol Attack Surface report, AI supply chain attack, and SEO poisoning targets VPNs
Nov 14, 2025
Highlights from the Zscaler ThreatLabz team's October 2025 research.
The CXO Monthly Roundup provides the latest Zscaler ThreatLabz research and critical updates, including the Mobile, IoT, & OT Threat Report, insights from the non-web Protocol Attack Surface Report, discovery of AI supply chain attack (CVE-2025-12058), and a new SEO poisoning campaign targeting VPN credentials.
Mobile, IoT, & OT Threat Report
The Zscaler ThreatLabz 2025 Mobile, IoT, & OT Threat Report showed an increase in threats across the cybersecurity landscape, with attackers focusing on core industries and leveraging reputable platforms to deliver malware. Our research team analyzed billions of blocked attacks within the Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange to reveal how attackers are targeting vulnerabilities across mobile devices, IoT environments, and the expanding ecosystem of cellular-connected IoT.
The key takeaways are:
- Android malware transactions increased by 67% year-over-year, fueled mainly by sophisticated spyware and banking trojans.
- ThreatLabz identified 239 malicious applications on the Google Play Store that were downloaded a collective 42 million times.
- IoT botnets remain dominant, with the Mirai, Mozi, and Gafgyt malware families accounting for 75% of all malicious IoT payloads.
- Attacks targeting the Energy sector increased by 387%, Transportation by 382%, and Healthcare by 224%.
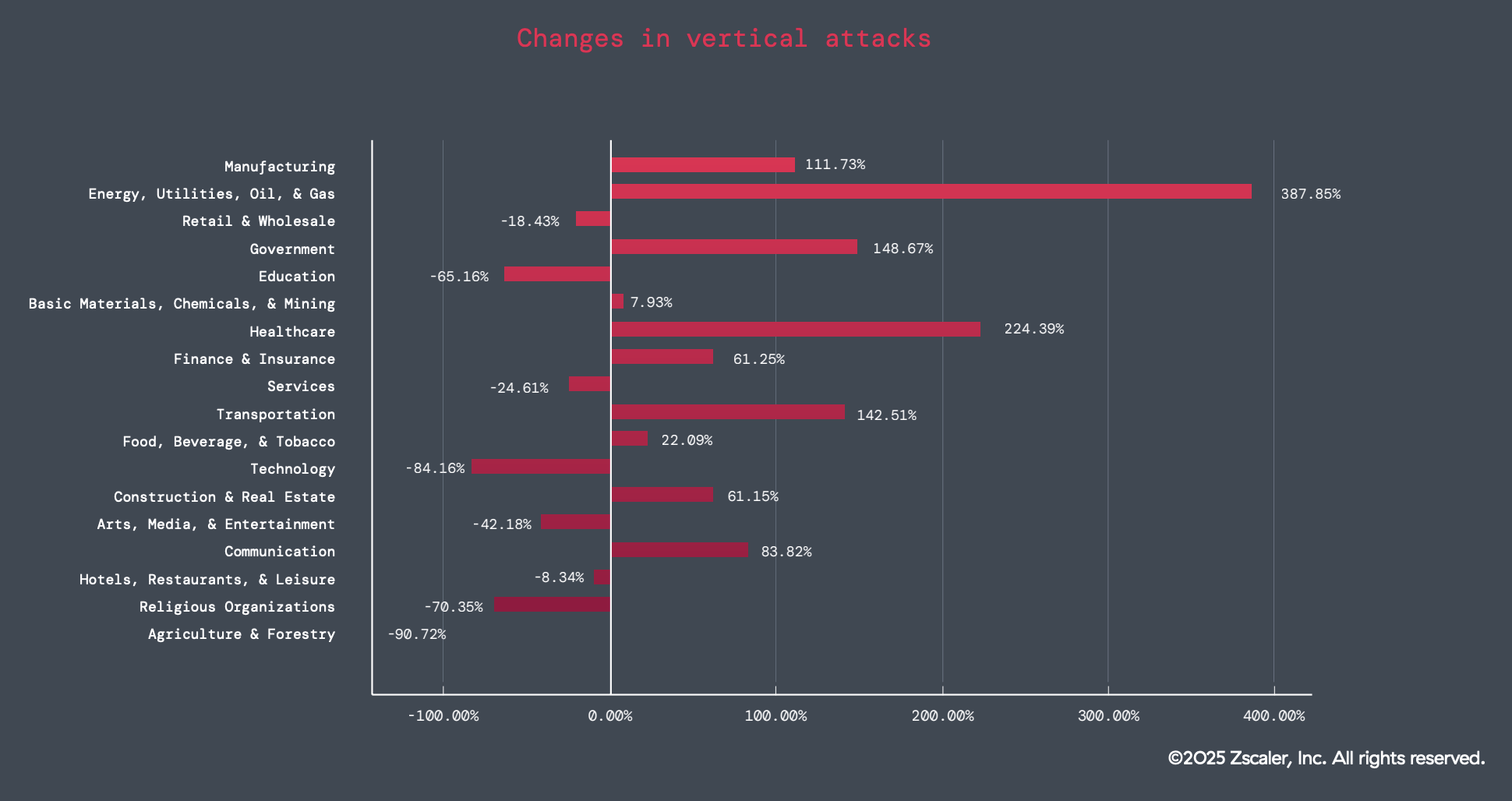
Figure 1: Graph depicting the changes in attacks across different sectors.
Defending against Mobile, IoT, & OT threats
To defend against threats such as these, organizations should adopt a comprehensive security approach with the following principles:
- Implement a zero trust architecture
- Discover and inventory all assets
- Enforce device segmentation and least-privilege access
- Prioritize patch management and system updates
- Deploy advanced threat detection and response
- Implement strong multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Educate and train employees on cybersecurity hygiene
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage – Advanced Cloud Sandbox, Advanced Threat Protection, Advanced Cloud Firewall, SSL Inspection, Zscaler Private Access, Zscaler Branch, Zscaler for IoT/OT (Device Segmentation), Zscaler Cellular
Non-Web Protocol Attack Surface Report
The Zscaler ThreatLabz 2025 Protocol Attack Surface Report revealed an increase in non-web protocol attacks, highlighting critical shifts in attacker methodologies. Key takeaways from the report include:
- 83.8% of non-web threats stem from DNS abuse, where attackers exploit protocols through tunneling, DGAs, and dynamic updates for data exfiltration and covert C2 communication.
- RDP accounts for 90.3% of brute force traffic, as attackers exploit weak authentication measures to breach systems and propagate ransomware. SMBv1 also remains a target, with attackers exploiting legacy vulnerabilities to launch zero-day exploits and facilitate lateral movements within systems.
- Sectors such as energy (61.1%) and manufacturing (76.1%) are prime targets for attackers leveraging SSH to establish footholds, anonymize activity, and maintain persistence.
- Anonymizer tools, predominantly Psiphon and Tor, are frequently used to obscure attacker activities.
- Retail remains the most targeted sector (62% of observed attacks).
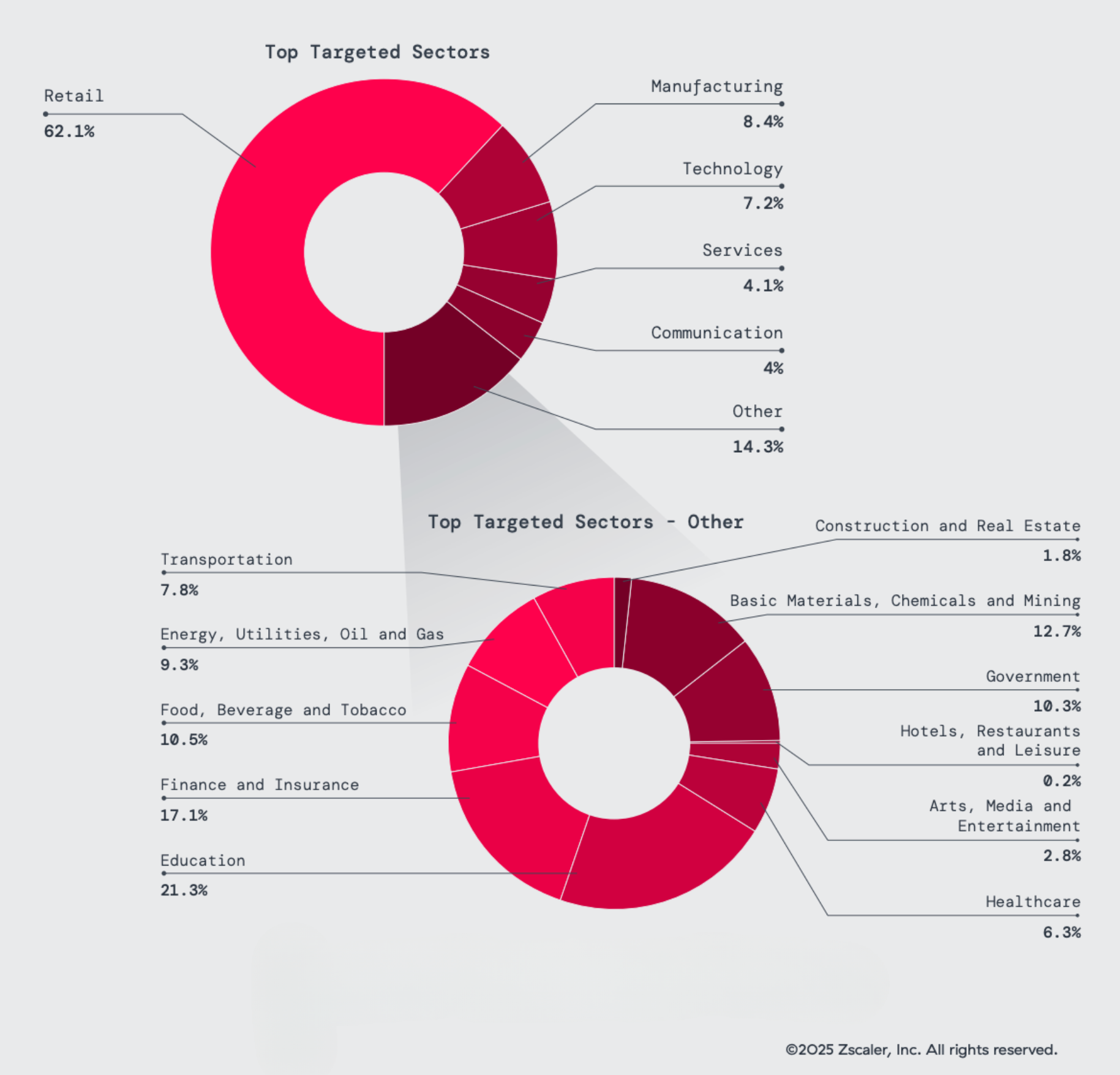
Figure 2: Top targeted sectors overall (top) and a detailed breakdown of the “‘other” category.
Securing Non-Web Protocols with Zscaler Zero Trust Firewall
As attackers exploit non-web protocols, traditional perimeter and legacy defenses leave organizations vulnerable. The Zscaler Zero Trust Firewall provides the following protections:
- Blocks malicious DNS and tunneling
- Prevents real-time threats with IPS
- Disrupts anonymizer and covert tunnels
- Zero Trust access segmentation
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage – Advanced Cloud Firewall, DNS Security
Strengthening AI Supply Chain Security: CVE-2025-12058
As AI adoption accelerates across industries, so do the associated risks. ThreatLabz recently identified CVE-2025-12058, a vulnerability in Keras (versions 3.11.3 and earlier), that allows arbitrary file access and potential Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) when loading malicious .keras model files. The flaw exists in the StringLookup and IndexLookup preprocessing layers, which permit file paths or URLs in their vocabulary parameter. When loading a serialized model (.keras file), Keras reconstructs these layers and accesses the referenced paths during deserialization - even with safe_mode=True enabled.
While Keras resolved this issue in version 3.11.4, I wanted to reiterate the importance of securing the AI model supply chain. The key business risks associated with unprotected AI supply chains that CISOs should be aware of are:
- Public or third-party model repositories may unintentionally propagate model files containing vulnerabilities or malicious configurations.
- Models loaded in virtual machines or containers could be used to access metadata endpoints, exposing cloud IAM credentials.
- Pre-trained models imported into development workflows could lead to unintended data exposure or backdoor insertion.
Guidance for CISOs
To help defend against CVE-2025-12058, I recommend CISOs take the following steps to strengthen their security posture and protect their AI ecosystem:
- Ensure your teams understand the types of vulnerabilities introduced by AI applications and frameworks.
- Develop processes to validate and monitor third-party and pre-trained models for security risks before they are integrated into workflows.
- Incorporate tools, such as Zscaler AISPM and AI Guard, that specialize in identifying and mitigating AI-related risks.
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage – Zscaler AI Guard, Zscaler Data Protection & AISPM
SEO Poisoning Fuels VPN Credential Theft
The Zscaler Threat Hunting team identified a campaign using SEO poisoning to distribute a malicious Ivanti Pulse Secure VPN client. Through SEO poisoning, attackers manipulate search engine results to redirect unsuspecting users to malicious websites, tricking them into downloading malware. In this case, attackers manipulated Bing search results to redirect users to fake Ivanti download pages. When the user opens the page, a trojanized installer is downloaded to their system, which steals VPN credentials by targeting the connectionstore.dat file and exfiltrates data to a Microsoft Azure-hosted command-and-control (C2) server. These credentials can facilitate further network breaches, including ransomware like Akira.
Key highlights of the campaign include:
- Attackers use lookalike domains and signed MSI installers to evade detection.
- Phishing sites deliver malicious content only when accessed via Bing search to bypass security checks.
- The malware parses VPN credentials, which can facilitate lateral movement within networks.
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage – Advanced Cloud Sandbox, Advanced Threat Protection, SSL Inspection, Zscaler Private Access
Recommended
