
EDITOR'S PICK
CISO Monthly Roundup, January 2024: Zero day VPN vulnerabilities, DreamBus, ZLoader, Qakbot, and recent security advisories
Feb 13, 2024
In the latest edition of the CISO Monthly Roundup we examine recent zero day VPN vulnerabilities and offer threat analysis on DreamBus, ZLoader, and Qakbot. We also take a look at recent security advisories and offer our insights.
The CISO Monthly Roundup provides the latest threat research from the ThreatLabz team, along with CISO insights on other cyber-related subjects. Over the past month ThreatLabz has examined Ivanti VPN vulnerabilities, performed a deep dive on Qakbot, analyzed new DreamBus modules, discovered new Zloader capabilities and addressed relevant security advisories.
Critical Risk Posed By Ivanti’s Zero-Day VPN Vulnerabilities
On January 19th CISA released an emergency directive (ED-24-01) setting a timeline for the mitigation of two known vulnerabilities in Ivanti VPN products (CVE-2023-46805 and CVE-2023-21887) . Ivanti released a patch, but threat actors were able to quickly circumvent the fix through exploiting two additional flaws (CVE-2024-21888 and CVE-2024-21893). This caused CISA to direct Federal Civilian Executive Branch agencies to stop using Ivanti Connect Secure (ICS) and Ivanti Policy Secure (IPS) solutions by 11:59 PM EST February 2, 2024.
There is strong suspicion that the Ivanti security flaws are being exploited by UTA0178, a government-backed threat group in China. Attackers are using the vulnerabilities to perform authentication bypass, command injection, and execute living-off-the-land attacks.
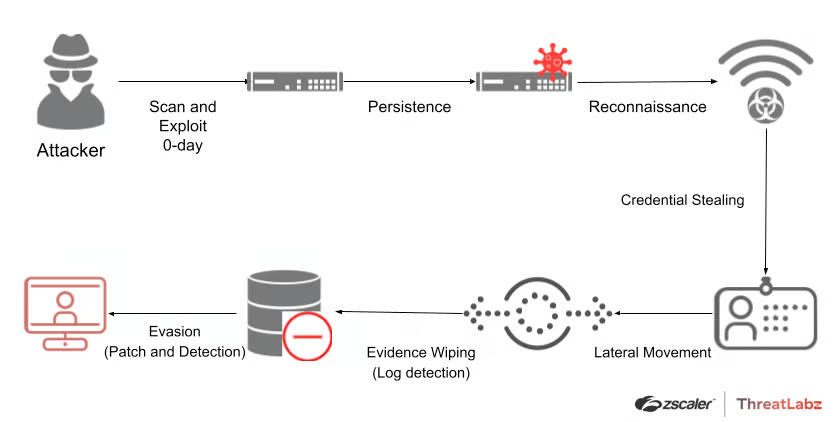
The attack chain used to exploit these vulnerabilities generally follows this pattern:
- Initial Exploitation: Attackers perform mass scanning for vulnerable devices
- Persistence: Attackers deployed different variations of web shells on the targeted devices. After gaining an initial foothold, they steal configuration data, modify existing files, download remote files, and reverse tunnel from the devices. They also backdoor configuration files and deploy additional tools
- Reconnaissance: Attackers perform reconnaissance of internal systems and applications through proxied connections
- Credential Stealing: Attackers inject a custom JavaScript-based malware into a login page to capture and exfiltrate plaintext user credentials
- Lateral Movement: Attackers use compromised credentials to laterally move through internal systems via RDP, SMB, and SSH.
- Evidence Wiping: Attackers wipe logs and restore systems to a clean state after deploying their payloads
- Evasion (Patch and Detection): Attackers modify the integrity checker tool (ICT) to prevent it from flagging any modifications or additions on the system
Zscaler customers are protected from these attacks on multiple levels, and can access secure connectivity without using VPN. Read our full blog on these vulnerabilities for a more complete breakdown of the associated risks and mitigations.
Read more about Ivanti VPN vulnerabilities
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage - Zscaler Internet Access (Advanced Cloud Sandbox, Advanced Threat Protection, SSL Inspection), Zscaler Private Access (App Protection & Deception)
DreamBus Unleashes Metabase Mayhem With New Exploit Module
The Zscaler ThreatLabz research team has identified new developments in the Linux-based DreamBus malware. While DreamBus has maintained a low profile, recent changes include two exploit modules targeting vulnerabilities in Metabase and Apache RocketMQ. The malware, active since 2019, exploits weak passwords and application-specific vulnerabilities to compromise systems, primarily for Monero cryptocurrency mining. The latest modifications aim to improve the malware’s success, as its reliance on older exploits was resulting in fewer infections.

Our technical analysis shows the complex nature of DreamBus modules. The Metabase exploit targets a command execution vulnerability. The Apache RocketMQ exploit allows remote command execution on RocketMQ versions 5.1.0 and earlier. These modules use sophisticated methods to evade detection and pose a threat to organizations. The Zscaler cloud platform detects DreamBus at various levels, keeping our customers secure. Organizations can also reduce their risk by reinforcing security measures such as strong passwords, multifactor authentication (MFA), and performing robust network monitoring.
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage - Zscaler Internet Access (Advanced Cloud Sandbox, Advanced Threat Protection, SSL Inspection), Zscaler Private Access (App Protection & Deception)
Zloader: No Longer Silent in the Night
Zloader, a modular trojan based on Zeus source code, resurfaced with notable updates after a two-year hiatus. Originally known as DELoader, this threat targeted German banks in 2016. Zloader ended its initial run in 2018, only to reappear in underground forums as Silent Night, in 2019. Zloader version 2.0.0.0 Was released around September 2021. Following a takedown in April 2022, Zloader returned with versions 2.1.x.x in September 2023.
The new version of Zloader introduces RSA encryption, 64-bit compatibility, an updated domain generation algorithm, and advanced obfuscation techniques. Zloader’s anti-analysis methods include API import hashing, junk code, filename checks, and string obfuscation. The trojan’s network communications now utilize 1024-bit RSA with RC4 and Zeus “visual encryption.” Our latest blog explores technical details of Zloader’s updates.
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage - Advanced Cloud Sandbox, Advanced Threat Protection, Advanced Cloud Firewall, SSL Inspection.
Tracking 15 Years of Qakbot Development
Our latest blog on Qakbot explores its 15-year evolution. This threat has transformed from a banking trojan to a versatile malware implanter, facilitating lateral movement and deploying ransomware. Despite law enforcement dismantling its infrastructure in August 2023, a new version emerged in December 2023, marking a development journey spanning over 15 years.

Qakbot’s trajectory, originating in 2008 as a banking trojan, centered on stealing credentials and conducting financial fraud. Recent adaptations transformed it into an initial access broker, facilitating lateral movement with tools like Cobalt Strike and leading to second-stage infections, including notable ransomware strains such as BlackBasta. Over time, Qakbot has evolved its anti-analysis techniques to evade various security measures. Its modular design allows for the dynamic addition of new functionalities through downloadable plugins. Notably, the threat group behind Qakbot has released 5 distinct versions, with the latest iteration released in December 2023. Qakbot’s 15-year progression, despite serious efforts to take down the operation by law officials, underscores the threat actor’s resilience and persistence.
Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange Coverage - Zscaler Internet Access (Advanced Cloud Sandbox, Advanced Threat Protection, SSL Inspection), Zscaler Private Access (App Protection & Deception)
Security Advisory:
Rise in Source IP-Based Authentication Abuse - Jan 19, 2024
The Zscaler ThreatLabz has observed an increase in attacks exploiting IP-based authentication. These attacks, leveraging system and identity compromise, target global entities, and if successful, can lead to unauthorized system access, data breaches, and compromise of data breaches. Common attack vectors include: system compromise, Wi-Fi network vulnerabilities, identity manipulation, physical access, misconfigurations, and unmanaged shadow IT. environments
Zscaler recommends a Zero Trust architecture, including granular access controls, posture control, and Data Loss Prevention policies. Additionally, using an Identity Provider (IdP) with FIDO2-based multi-factor authentication (MFA) and reinforcing user account reset processes can further mitigate vulnerabilities associated with IP-based authentication.
Apache OFBiz Authentication Bypass Vulnerability (CVE-2023-51467)
Researchers at SonicWall uncovered a critical zero-day security flaw, CVE-2023-51467, in Apache OFBiz, enabling authentication bypass and Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF). A previous patch for CVE-2023-49070 failed to address the root cause, leaving the vulnerability unresolved. Users are urged to upgrade to Apache OFBiz version 18.12.11 immediately. Affected versions include 18.12.10 and below for CVE-2023-51467 and 18.12.9 and below for CVE-2023-49070. The flaw involves manipulating login parameters to achieve Remote Code Execution (RCE). Zscaler recommends best practices to mitigate risks, emphasizing application security, traffic routing through Zscaler, and implementing advanced threat protection. Failure to update may expose systems to potential exploits.
About ThreatLabz
ThreatLabz is the embedded research team at Zscaler. This global team includes security experts, researchers, and network engineers responsible for analyzing and eliminating threats across the Zscaler security cloud and investigating the global threat landscape. The team shares its research and cloud data with the industry at large to help promote a safer internet.
The Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange
Zscaler manages the world’s largest security cloud. Each day, Zscaler blocks over 150 million threats to its 7300+ customers, securing over 300 billion web transactions daily. The Zscaler ThreatLabz security research team uses state-of-the-art AI/ML and machine-learning technology to analyze Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange traffic and share its findings.
What to read next:
2023 ThreatLabz State of Ransomware report
Recommended
