Zscaler Blog
Get the latest Zscaler blog updates in your inbox
Exploring Encrypted Attacks Amidst the AI Revolution
Introduction
Zscaler ThreatLabz researchers analyzed 29.8 billion blocked threats embedded in encrypted traffic from October 2022 to September 2023 in the Zscaler cloud, presenting their findings in the Zscaler ThreatLabz 2023 State of Encrypted Attacks Report. In addition to the blocked threats, this report leverages insights from 500 trillion daily signals and 360 billion daily transactions in the Zscaler Zero Trust Exchange™. In this blog post, we’ll unpack key findings from the report.
Encrypted Attacks
According to the Google Transparency Report1, encrypted traffic saw a significant rise in the last decade, reaching 95% of global traffic today compared to 48% in December 2013. It’s no surprise that encrypted traffic, once hailed as the secure choice for online activities, now also harbors the majority of cyber threats – like malware, phishing scams, and data leaks.
85.9% of Attacks are Encrypted
Almost 86% of attacks use encrypted channels across various stages of the kill chain. From the initial phases of phishing and malware delivery to the subtleties of command-and-control activities as well as data exfiltration, cybercriminals leverage encryption to shield their intentions. To combat this, Zscaler recommends organizations proactively inspect all encrypted traffic to detect, decrypt, and thwart these attacks.
78.1% of Encrypted Threats Involve Malware
Cybercriminals conceal a variety of threats in encrypted traffic. However, malware remains the predominant threat type, comprising 78.1% of encrypted attacks blocked by the Zscaler cloud, including malicious scripts, payloads, web content, websites, and email attachments.
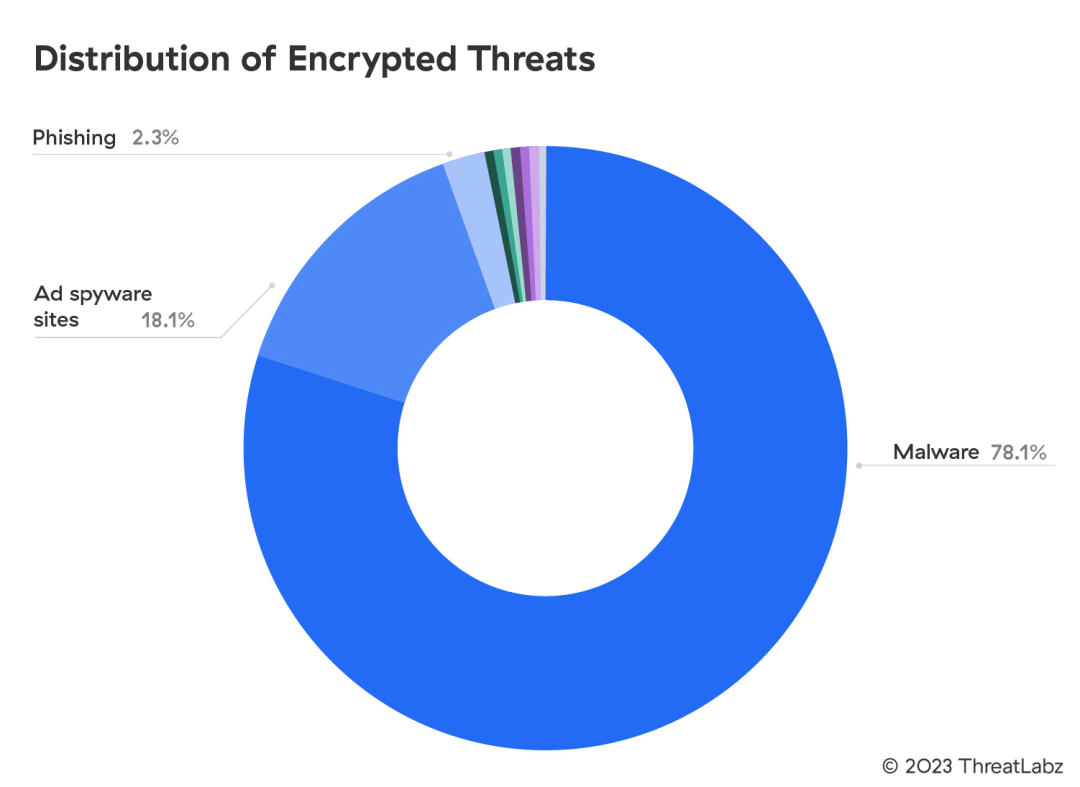
Figure 1: Distribution of encrypted threats
The surge in encrypted malware blocks highlights the trend where these threat actors are trying to establish an initial foothold in the victim environment by evading legacy detection technologies that often struggle to inspect TLS traffic at scale.
Phishing Increased by 13.7%
The growth observed in phishing attacks is likely powered by the availability of AI tools and plug-and-play phishing services (aka Phishing-as-a-Service offerings) making it that much easier to execute phishing campaigns.
Five of the most phished brands involve:
- Microsoft
- OneDrive
- Sharepoint
- Adobe
- Amazon
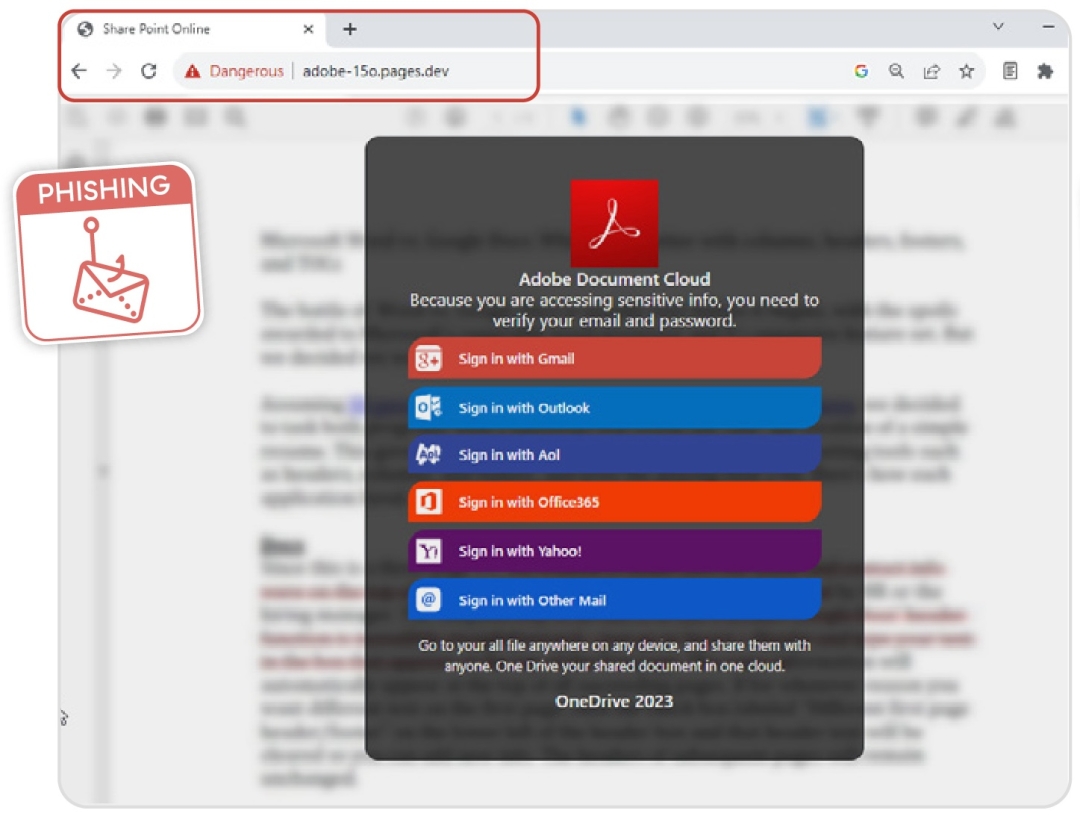
Figure 2: Adobe-themed phishing campaign
Manufacturing Still the Most Targeted Sector
Manufacturing remains the most targeted industry, experiencing 31.6% of encrypted attacks.
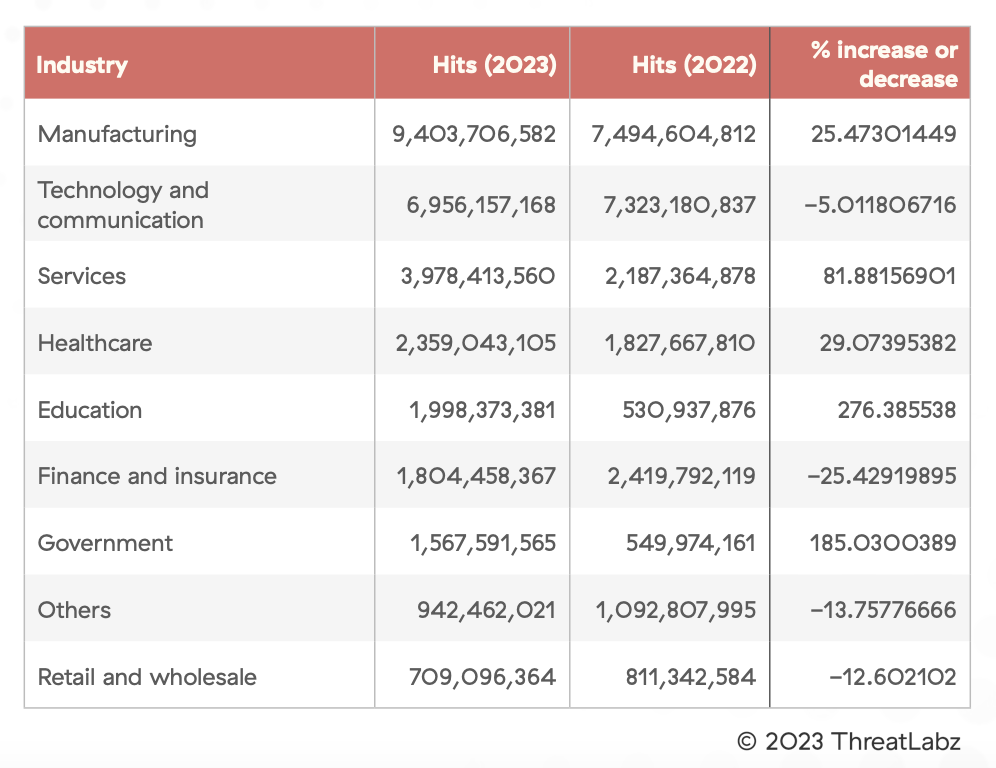
Figure 3: A table showing encrypted attack trends by industry
Manufacturers also saw the largest amount of AI/ML transactions compared to any other industry processing over 2.1 billion AI/ML-related transactions. As smart factories and the Internet of Things (IoT) become more prevalent in manufacturing, the attack surface is expanding and exposing the sector to more security risks and creating additional entry points that cybercriminals can exploit to disrupt production and supply chains. The use of popular generative AI applications, like ChatGPT, on connected devices in manufacturing heightens the risk of sensitive data leakage over encrypted channels.
Zscaler Secures Organizations Against Encrypted Attacks at Scale
The report’s main takeaway is this: if you’re not looking at encrypted channels, you don’t know if you’re suffering data leaks or if advanced threats are entering your environment. To help our customers stay secure, Zscaler blocked nearly 30 billion threats over encrypted channels in 2023—a 24.3% increase from the 24 billion blocked in 2022.
Today, most attacks leverage SSL or TLS encryption, which is resource-intensive to inspect at scale and best done with a cloud native proxy architecture. While legacy firewalls support packet filtering and stateful inspection, their resource limitations make them poorly suited for this task. This creates a critical need for organizations to implement cloud native architectures that support full inspection of encrypted traffic in alignment with zero trust principles.
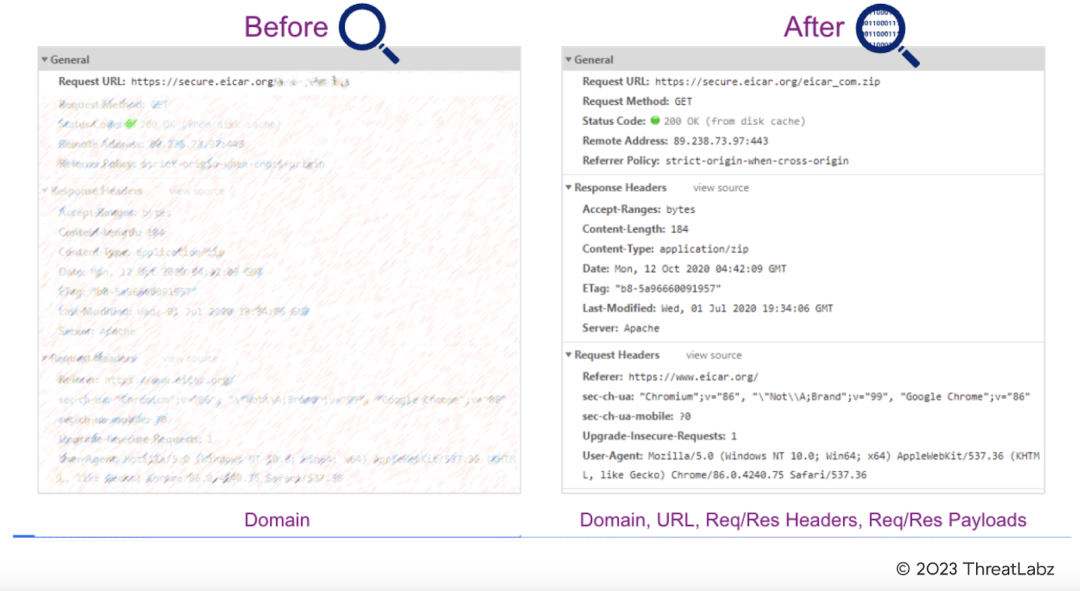
Figure 4: TLS inspection provides full visibility to block advanced threats
How Zscaler Helps Mitigate Encrypted Attacks
Deepen Desai, Chief Security Officer, Zscaler, says:
“While 95% of web traffic is encrypted with HTTPS, we are seeing that the large majority of threats are now delivered over encrypted channels. As a result, any traffic encrypted with SSL/TLS that does not undergo inline inspection to defend against the full gamut of threats can pose a significant risk to global organizations.”
Desai recommends the following solutions to protect your organization from encrypted attacks consistently:
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) - Disrupt as many stages of this attack chain as possible, maximizing your chances of stopping the attack even if the threat actors evade some of your security controls. I recommend replacing vulnerable appliances like VPNs and firewalls with ZTNA to inspect and scan 100% of SSL/TLS traffic.
- Zscaler Private Access (ZPA) - Implement consistent security with enhanced segmentation, connecting users to applications, not the entire network. ZPA is designed to provide secure and direct access for users to specific applications, ensuring that network traffic is segmented, and users don’t have access to the entire network.
- Zscaler Cloud Data Loss Prevention (DLP) - Integrate Zscaler Cloud DLP as an in-line data loss prevention technology with full TLS inspection to prevent sensitive data leakage.
Best Practices for Mitigating Encrypted Attacks
Your cybersecurity strategy should include controls for each of these stages:
- Minimize the attack surface by making internal apps invisible to the internet.
- Prevent compromise by using cloud native proxy architecture to inspect all traffic inline and at scale, enforcing consistent security policies.
- Stop lateral movement by connecting users directly to applications (rather than the network) to reduce the attack surface, and contain threats by using deception and workload segmentation.
- Stop data loss by inspecting all internet-bound traffic, including encrypted channels, to prevent data theft.
If you’re looking to minimize the risk of encrypted attacks for your organization, you should consider these recommendations as part of your adoption strategy:
- Use a cloud native, proxy-based architecture to decrypt, detect, and prevent threats in all encrypted traffic at scale.
- Leverage an AI-driven sandbox to quarantine unknown attacks and stop patient zero malware.
- Inspect all traffic, all the time, whether a user is at home, at headquarters, or on the go, to ensure everyone is consistently protected against encrypted threats.
- Terminate every connection to allow an inline proxy architecture to inspect all traffic, including encrypted traffic, in real-time—before it reaches its destination—to prevent ransomware, malware, and more.
- Protect data using granular context-based policies, verifying access requests and rights based on context.
- Eliminate the attack surface by connecting users directly to the apps and resources they need, never to networks.
Best Practices for Safe AI/ML Interactions
Considering the rapid advancement and adoption of AI-powered applications, it is crucial to establish and follow best practices to ensure the responsible and secure use of these transformative technologies.
- Organizations must proactively adapt their AI usage and security policies to stay ahead of potential risks and challenges.
- Implement TLS inspection for public AI chatbot applications like ChatGPT using granular DLP policies to prevent sensitive data leakage.
- Ensure that the use of AI tools complies with all relevant laws and ethical standards. This includes data protection regulations and privacy laws.
- Establish clear accountability for the development and deployment of AI tools. Define roles and responsibilities within your organization to oversee AI projects.
- The development and integration of AI tools should follow a Secure Product Lifecycle Framework to guarantee the highest level of security.
Learn More
Download your copy of the full Zscaler ThreatLabz 2023 State of Encrypted Attacks Report to discover more insights and advice for managing encrypted attacks.
1. https://transparencyreport.google.com/https/overview?hl=en
Was this post useful?
Disclaimer: This blog post has been created by Zscaler for informational purposes only and is provided "as is" without any guarantees of accuracy, completeness or reliability. Zscaler assumes no responsibility for any errors or omissions or for any actions taken based on the information provided. Any third-party websites or resources linked in this blog post are provided for convenience only, and Zscaler is not responsible for their content or practices. All content is subject to change without notice. By accessing this blog, you agree to these terms and acknowledge your sole responsibility to verify and use the information as appropriate for your needs.
Get the latest Zscaler blog updates in your inbox
By submitting the form, you are agreeing to our privacy policy.



