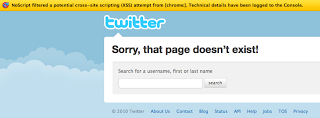
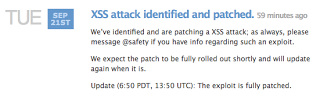
This morning before I even logged into my system, I was receiving inquiries about the Twitter Spam going around. The source looks like:
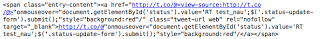
And appears in Twitter as:
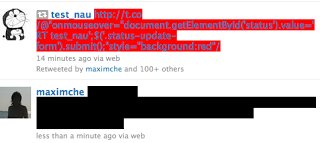
For those unfamiliar with t.co, it is Twitter's link service, which provides URL shortening as well as checks to ensure that the link doesn't go to a known malicious site (see About Twitter's Link Service for more info). You can see from the source of the tweet, that it is leveraging a cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability so that the scripting code following the "@" character is executed within the victim's browser, and just by mousing over the tweet you are retweeting it. The tweet name / retweet value varies. (a.no has been seen in addition to the t.co domain).
Doing a Twitter search for "Onmouseover" provides a laundry list of URLs and "victims" of this spam. The results of the spam campaign are tweet spam (annoyance) and a likely strain on Twitter services from the increase in retweets. After doing a Twitter search, after a few minutes, the search results showed over 30K more tweets since my initial search - this illustrates how rapidly spreading the XSS retweet spam is being spread.
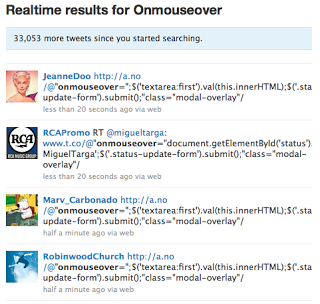 Digging a bit deeper into this reveals that it was an Australian teenager going by the handle zzap that discovered the XSS vulnerability whereby arbitrary script following the "@" character is executed (ref. NetCraft). Cross-site request forgery and cookie stealing attacks have been demonstrated leveraging the XSS vulnerability as well. Currently there are a number of Twitter worms leveraging this vulnerability (ref. F-Secure).
Digging a bit deeper into this reveals that it was an Australian teenager going by the handle zzap that discovered the XSS vulnerability whereby arbitrary script following the "@" character is executed (ref. NetCraft). Cross-site request forgery and cookie stealing attacks have been demonstrated leveraging the XSS vulnerability as well. Currently there are a number of Twitter worms leveraging this vulnerability (ref. F-Secure).
Some security precautions for users to consider:
- Avoid accessing your Twitter account from a browser, consider using a Twitter client
- If accessing your account via browser turn off JavaScript or use NoScript